Differential expression of I(A) channel subunits Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 in mouse visual cortical neurons and synapses
- PMID: 17122053
- PMCID: PMC6675432
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2599-06.2006
Differential expression of I(A) channel subunits Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 in mouse visual cortical neurons and synapses
Abstract
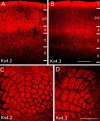
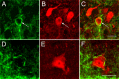
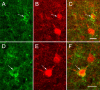
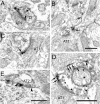
In cortical neurons, pore-forming alpha-subunits of the Kv4 subfamily underlie the fast transient outward K+ current (I(A)). Considerable evidence has accumulated demonstrating specific roles for I(A) channels in the generation of individual action potentials and in the regulation of repetitive firing. Although I(A) channels are thought to play a role in synaptic processing, little is known about the cell type- and synapse-specific distribution of these channels in cortical circuits. Here, we used immunolabeling with specific antibodies against Kv4.2 and Kv4.3, in combination with GABA immunogold staining, to determine the cellular, subcellular, and synaptic localization of Kv4 channels in the primary visual cortex of mice, in which subsets of pyramidal cells express yellow fluorescent protein. The results show that both Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 are concentrated in layer 1, the bottom of layer 2/3, and in layers 4 and 5/6. In all layers, clusters of Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 immunoreactivity are evident in the membranes of the somata, dendrites, and spines of pyramidal cells and GABAergic interneurons. Electron microscopic analyses revealed that Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 clusters in pyramidal cells and interneurons are excluded from putative excitatory synapses, whereas postsynaptic membranes at GABAergic synapses often contain Kv4.2 and Kv4.3. The presence of Kv4 channels at GABAergic synapses would be expected to weaken inhibition during dendritic depolarization by backpropagating action potentials. The extrasynaptic localization of Kv4 channels near excitatory synapses, in contrast, should stabilize synaptic excitation during dendritic depolarization. Thus, the synapse-specific distribution of Kv4 channels functions to optimize dendritic excitation and the association between presynaptic and postsynaptic activity.
Figures





References
-
- Alonso G, Widmer H. Clustering of Kv4.2 potassium channels in postsynaptic membrane of rat supraoptic neurons: an ultrastructural study. Neuroscience. 1997;77:617–621. - PubMed
-
- Cai X, Liang CW, Muralidharan S, Kao JPY, Tang C-M, Thompson SM. Unique roles of SK and Kv4.2 potassium channels in dendritic integration. Neuron. 2004;44:351–364. - PubMed
-
- Chu P-J, Rivera JF, Arnold DB. A role for Kif17 in transport of Kv4.2. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:365–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
