Neurotransmitter depletion by bafilomycin is promoted by vesicle turnover
- PMID: 17123716
- PMCID: PMC6930131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.10.040
Neurotransmitter depletion by bafilomycin is promoted by vesicle turnover
Abstract
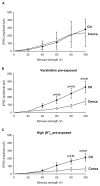
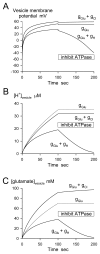
Accumulation of neurotransmitter into synaptic vesicles is powered by the vacuolar proton ATPase. We show here that, in brain slices, application of the H(+)-ATPase inhibitors bafilomycin or concanamycin does not efficiently deplete glutamatergic vesicles of transmitter unless vesicle turnover is increased. Simulations of vesicle energetics suggest either that bafilomycin and concanamycin act on the H(+)-ATPase from inside the vesicle, or that the vesicle membrane potential is maintained after the H(+)-ATPase is inhibited.
Figures

References
-
- Bai L, Xu H, Collins JF, Ghishan FK. Molecular and functional analysis of a novel neuronal vesicular glutamate transporter. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36764–36769. - PubMed
-
- Bellocchio EE, Reimer RJ, Fremeau RT, Jr, Edwards RH. Uptake of glutamate into synaptic vesicles by an inorganic phosphate transporter. Science. 2000;289:957–960. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

