Prevalence of the initiator over the TATA box in human and yeast genes and identification of DNA motifs enriched in human TATA-less core promoters
- PMID: 17123746
- PMCID: PMC1955227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.09.029
Prevalence of the initiator over the TATA box in human and yeast genes and identification of DNA motifs enriched in human TATA-less core promoters
Abstract
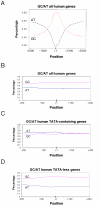
The core promoter of eukaryotic genes is the minimal DNA region that recruits the basal transcription machinery to direct efficient and accurate transcription initiation. The fraction of human and yeast genes that contain specific core promoter elements such as the TATA box and the initiator (INR) remains unclear and core promoter motifs specific for TATA-less genes remain to be identified. Here, we present genome-scale computational analyses indicating that approximately 76% of human core promoters lack TATA-like elements, have a high GC content, and are enriched in Sp1-binding sites. We further identify two motifs - M3 (SCGGAAGY) and M22 (TGCGCANK) - that occur preferentially in human TATA-less core promoters. About 24% of human genes have a TATA-like element and their promoters are generally AT-rich; however, only approximately 10% of these TATA-containing promoters have the canonical TATA box (TATAWAWR). In contrast, approximately 46% of human core promoters contain the consensus INR (YYANWYY) and approximately 30% are INR-containing TATA-less genes. Significantly, approximately 46% of human promoters lack both TATA-like and consensus INR elements. Surprisingly, mammalian-type INR sequences are present - and tend to cluster - in the transcription start site (TSS) region of approximately 40% of yeast core promoters and the frequency of specific core promoter types appears to be conserved in yeast and human genomes. Gene Ontology analyses reveal that TATA-less genes in humans, as in yeast, are frequently involved in basic "housekeeping" processes, while TATA-containing genes are more often highly regulated, such as by biotic or stress stimuli. These results reveal unexpected similarities in the occurrence of specific core promoter types and in their associated biological processes in yeast and humans and point to novel vertebrate-specific DNA motifs that might play a selective role in TATA-independent transcription.
Figures





References
-
- Aso T, Conaway JW, Conaway RC. Role of core promoter structure in assembly of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. A common pathway for formation of preinitiation intermediates at many TATA and TATA-less promoters. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:26575–26583. - PubMed
-
- Bajic VB, Choudhary V, Hock CK. Content analysis of the core promoter region of human genes. In Silico Biol. 2004;4:109–125. - PubMed
-
- Basehoar AD, Zanton SJ, Pugh BF. Identification and distinct regulation of yeast TATA box-containing genes. Cell. 2004;116:699–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

