Impaired neural development caused by inducible expression of Axin in transgenic mice
- PMID: 17123792
- PMCID: PMC1847614
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mod.2006.10.002
Impaired neural development caused by inducible expression of Axin in transgenic mice
Abstract
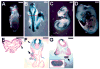
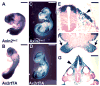
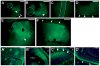
Ablations of the Axin family genes demonstrated that they modulate Wnt signaling in key processes of mammalian development. The ubiquitously expressed Axin1 plays an important role in formation of the embryonic neural axis, while Axin2 is essential for craniofacial skeletogenesis. Although Axin2 is also highly expressed during early neural development, including the neural tube and neural crest, it is not essential for these processes, apparently due to functional redundancy with Axin1. To further investigate the role of Wnt signaling during early neural development, and its potential regulation by Axins, we developed a mouse model for conditional gene activation in the Axin2-expressing domains. We show that gene expression can be successfully targeted to the Axin2-expressing cells in a spatially and temporally specific fashion. High levels of Axin in this domain induce a region-specific effect on the patterning of neural tube. In the mutant embryos, only the development of midbrain is severely impaired even though the transgene is expressed throughout the neural tube. Axin apparently regulates beta-catenin in coordinating cell cycle progression, cell adhesion and survival of neuroepithelial precursors during development of ventricles. Our data support the conclusion that the development of embryonic neural axis is highly sensitive to the level of Wnt signaling.
Figures




References
-
- Behrens J, Jerchow BA, Wurtele M, Grimm J, Asbrand C, Wirtz R, Kuhl M, Wedlich D, Birchmeier W. Functional interaction of an axin homolog, conductin, with beta-catenin, APC, and GSK3beta. Science. 1998;280:596–599. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W. Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 1996;382:638–642. - PubMed
-
- Bhanot P, Brink M, Samos CH, Hsieh JC, Wang Y, Macke JP, Andrew D, Nathans J, Nusse R. A new member of the frizzled family from Drosophila functions as a Wingless receptor. Nature. 1996;382:225–330. - PubMed
-
- Bienz M. β-Catenin: a pivot between cell adhesion and Wnt signalling. Curr Biol. 2005;15:R64–R67. - PubMed
-
- Boutros M, Paricio N, Strutt DI, Mlodzik M. Dishevelled activates JNK and discriminates between JNK pathways in planar polarity and wingless signaling. Cell. 1998;94:109–118. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

