Efficacy of three artemisinin combination therapies for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in the Republic of Congo
- PMID: 17125496
- PMCID: PMC1697822
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-5-113
Efficacy of three artemisinin combination therapies for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in the Republic of Congo
Abstract
Background: Presented here are the results of a comparative trial on the efficacy of three artemisinin-based combinations conducted from May to October 2004, in Pool Province, Republic of Congo.
Methods: The main outcome was the proportion of cases of true treatment success at day 28. Recrudescences were distinguished from re-infections by PCR analysis. A total of 298 children of 6-59 months were randomized to receive either artesunate + SP (AS+SP), artesunate + amodiaquine (AS+AQ) or artemether + lumefantrine (AL), of which 15 (5%) were lost to follow-up.
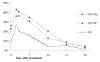
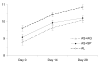
Results: After 28 days, there were 21/85 (25%) recurrent parasitaemias in the AS+SP group, 31/97 (32%) in the AS+AQ group and 13/100 (13%) in the AL group. The 28-day PCR-corrected cure rate was 90.1% [95% CI 80.7-95.9] for AS+SP, 98.5% [95% CI 92.0-100] for AS+AQ and 100% [95.8-100] for AL, thereby revealing a weaker response to AS+SP than to AL (p = 0.003) and to AS+AQ (p = 0.06). A potential bias was the fact that children treated with AL were slightly older and in better clinical condition, but logistic regression did not identify these as relevant factors. There was no significant difference between groups in fever and parasite clearance time, improvement of anaemia and gametocyte carriage at day 28. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: Considering the higher efficacy of AL as compared to AS+SP and the relatively high proportion of cases with re-infections in the AS+AQ group, we conclude that AL is clinically more effective than AS+SP and AS+AQ in this area of the Republic of Congo. Implementation of the recently chosen new national first-line AS+AQ should be monitored closely.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Africa malaria report. WHO/CDS/MAL Geneva 1093, Switzerland; 2003.
-
- WHO . Profil pays environnements sains pour les enfants. Bureau du Répresentant de l'OMS pour le Congo, Brazzaville; 2003.
-
- PNLP Powerpoint presentation- 'Activités de prise en charge'. 2005. http://www.RACTP.org
-
- WHO . Susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum to antimalarial drugs. Report on global monitoring:1996–2004. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland; 2005.
-
- Nsimba B, Malonga DA, Mouata AM, Louya F, Kiori J, Malanda M, Yocka D, Oko-Ossho J, Ebata-Mongo S, Le Bras J. Efficacy of sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Republic of Congo. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70:133–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials