Remembering the past and imagining the future: common and distinct neural substrates during event construction and elaboration
- PMID: 17126370
- PMCID: PMC1894691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.10.016
Remembering the past and imagining the future: common and distinct neural substrates during event construction and elaboration
Abstract
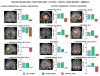
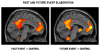
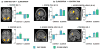
People can consciously re-experience past events and pre-experience possible future events. This fMRI study examined the neural regions mediating the construction and elaboration of past and future events. Participants were cued with a noun for 20s and instructed to construct a past or future event within a specified time period (week, year, 5-20 years). Once participants had the event in mind, they made a button press and for the remainder of the 20s elaborated on the event. Importantly, all events generated were episodic and did not differ on a number of phenomenological qualities (detail, emotionality, personal significance, field/observer perspective). Conjunction analyses indicated the left hippocampus was commonly engaged by past and future event construction, along with posterior visuospatial regions, but considerable neural differentiation was also observed during the construction phase. Future events recruited regions involved in prospective thinking and generation processes, specifically right frontopolar cortex and left ventrolateral prefrontal cortex, respectively. Furthermore, future event construction uniquely engaged the right hippocampus, possibly as a response to the novelty of these events. In contrast to the construction phase, elaboration was characterized by remarkable overlap in regions comprising the autobiographical memory retrieval network, attributable to the common processes engaged during elaboration, including self-referential processing, contextual and episodic imagery. This striking neural overlap is consistent with findings that amnesic patients exhibit deficits in both past and future thinking, and confirms that the episodic system contributes importantly to imagining the future.
Figures

References
-
- Addis DR, McIntosh AR, Moscovitch M, Crawley AP, McAndrews MP. Characterizing spatial and temporal features of autobiographical memory retrieval networks: a partial least squares approach. Neuroimage. 2004;23:1460–1471. - PubMed
-
- Addis DR, Moscovitch M, Crawley AP, McAndrews MP. Recollective qualities modulate hippocampal activation during autobiographical memory retrieval. Hippocampus. 2004;14:752–762. - PubMed
-
- Atance CM, O’Neill DK. Episodic future thinking. Trends Cogn Sci. 2001;5(12):533–539. - PubMed
-
- Atance CM, O’Neill DK. The emergence of episodic future thinking in humans. Learning and Motivation. 2005;36:126–144.
-
- Bar M, Aminoff E. Cortical analysis of visual context. Neuron. 2003;38:347–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

