Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: to operate or not to operate?
- PMID: 17127707
- PMCID: PMC1955529
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.100628
Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: to operate or not to operate?
Abstract
Background: Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (BD-IPMNs) of the pancreas are reported to be less aggressive than the main-duct type. Hence, less aggressive treatment has been proposed for the former.
Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness of a follow-up protocol for BD-IPMNs.
Design: Prospective study.
Setting: An academic tertiary referral centre.
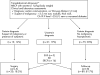
Patients: From 2000 to 2003, 109 patients with BD-IPMNs underwent trans-abdominal ultrasound and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with secretin. Patients who presented malignancy-related parameters (size >3.5 cm, nodules, thick walls, carbohydrate antigen 19.9 level >25 U/l, recent-onset or worsened diabetes) and/or complained of symptoms were submitted to surgery (arm A). All asymptomatic patients without suspicion of malignancy were followed up according to a 6-month clinical-radiological protocol (arm B).
Main outcome measures: The effectiveness of conservative management of BD-IPMNs.
Results: 20 (18.3%) patients underwent surgery (arm A); pathological diagnosis of BD-IPMNs was always confirmed. 89 (81.7%) patients were followed up for a median of 32 months (arm B); of these, 57 (64%) patients had multifocal disease. After a mean follow-up of 18.2 months, 5 (5.6%) patients showed an increase in lesion size and underwent surgery. The pathological diagnosis was branch-duct adenoma in three patients and borderline adenoma in two.
Conclusions: Surgery is indicated in <20% of cases of BD-IPMNs, and, in the absence of malignancy-related parameters, careful non-operative management seems to be safe and effective in asymptomatic patients. Although observation for a longer time is needed to confirm these results, our findings support the guidelines recently recommended by the International Association of Pancreatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Comment in
-
A new approach to managing intraductal papillary mucinous pancreatic neoplasms.Gut. 2007 Aug;56(8):1041-4. doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.113068. Gut. 2007. PMID: 17625140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kloppel G S E, Longnecker D S, Capella C.et al Histogical typing of tumours of the esocrine pancreas. World Health Organization international histological classification of tumours. Berlin: Springer‐Verlag, 1996
-
- Longnecker D S, Adler G, Hruban H R.et al Intraductal papillary‐mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. In: Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA, eds. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC Press, 1999237–240.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical