Small interfering RNA targeted to stem-loop II of the 5' untranslated region effectively inhibits expression of six HCV genotypes
- PMID: 17129382
- PMCID: PMC1698915
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-3-100
Small interfering RNA targeted to stem-loop II of the 5' untranslated region effectively inhibits expression of six HCV genotypes
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Small interfering RNA targeted to stem-loop II of the 5' untranslated region effectively inhibits expression of six HCV genotypes.Virol J. 2021 Jul 26;18(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01623-y. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 34311743 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The antiviral action of interferon alpha targets the 5' untranslated region (UTR) used by hepatitis C virus (HCV) to translate protein by an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) mechanism. Although this sequence is highly conserved among different clinical strains, approximately half of chronically infected hepatitis C patients do not respond to interferon therapy. Therefore, development of small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeted to the 5'UTR to inhibit IRES mediated translation may represent an alternative approach that could circumvent the problem of interferon resistance.
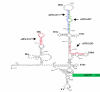
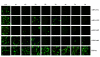
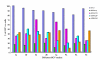
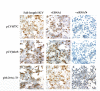
Results: Four different plasmid constructs were prepared for intracellular delivery of siRNAs targeting the stem loop II-III of HCV 5' UTR. The effect of siRNA production on IRES mediated translation was investigated using chimeric clones between the gene for green fluorescence protein (GFP) and IRES sequences of six different HCV genotypes. The siRNA targeted to stem loop II effectively mediated degradation of HCV IRES mRNA and inhibited GFP expression in the case of six different HCV genotypes, where as siRNAs targeted to stem loop III did not. Furthermore, intracytoplasmic expression of siRNA into transfected Huh-7 cells efficiently degraded HCV genomic RNA and inhibited core protein expression from infectious full-length infectious clones HCV 1a and HCV 1b strains.
Conclusion: These in vitro studies suggest that siRNA targeted to stem-loop II is highly effective inhibiting IRES mediated translation of the major genotypes of HCV. Stem-loop II siRNA may be a good target for developing an intracellular immunization strategy based antiviral therapy to inhibit hepatitis C virus strains that are not inhibited by interferon.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Down-regulation of IRES containing 5'UTR of HCV genotype 3a using siRNAs.Virol J. 2011 May 13;8:221. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-221. Virol J. 2011. PMID: 21569449 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus small interfering RNA targeted to stem-loops II and III of IRES structure of 5' UTR effectively inhibits virus replication and translation of HCV sub-genotype 4a isolates from Saudi Arabia.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Jan;28(1):1109-1122. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.11.041. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33424405 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus IRES-mediated translation by small RNAs analogous to stem-loop structures of the 5'-untranslated region.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Mar 12;32(5):1678-87. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh328. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15020704 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotide-based strategies to inhibit human hepatitis C virus.Oligonucleotides. 2003;13(6):539-48. doi: 10.1089/154545703322860834. Oligonucleotides. 2003. PMID: 15025918 Review.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Translation Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 27;21(7):2328. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072328. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32230899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic implications of hepatitis C virus resistance to antiviral drugs.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2009 Jul;2(4):205-19. doi: 10.1177/1756283X09336045. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 21180544 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection: translational evasion of oxidative defence.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Mar 21;20(11):2785-800. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.2785. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24659872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinations of siRNAs against La Autoantigen with NS5B or hVAP-A Have Additive Effect on Inhibition of HCV Replication.Hepat Res Treat. 2016;2016:9671031. doi: 10.1155/2016/9671031. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Hepat Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27446609 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid nanoparticles as carriers for RNAi against viral infections: current status and future perspectives.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:161794. doi: 10.1155/2014/161794. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25184135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host-virus interaction: the antiviral defense function of small interfering RNAs can be enhanced by host microRNA-7 in vitro.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 12;5:9722. doi: 10.1038/srep09722. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26067353 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

