Hepatocellular proliferation in response to agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha: a role for Kupffer cells?
- PMID: 17129391
- PMCID: PMC1684246
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3163-5-26
Hepatocellular proliferation in response to agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha: a role for Kupffer cells?
Abstract
Background: It has been proposed that PPARalpha agonists stimulate Kupffer cells in rodents which in turn, release mitogenic factors leading to hepatic hyperplasia, and eventually cancer. However, Kupffer cells do not express PPARalpha receptors, and PPARalpha agonists stimulate hepatocellular proliferation in both TNFalpha- and TNFalpha receptor-null mice, casting doubt on the involvement of Kupffer cells in the mitogenic response to PPARalpha agonists. This study was therefore designed to investigate whether the PPARalpha agonist PFOA and the Kupffer cell inhibitor methylpalmitate produce opposing effects on hepatocellular proliferation and Kupffer cell activity in vivo, in a manner that would implicate these cells in the mitogenic effects of PPARalpha agonists.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were treated intravenously via the tail vein with methylpalmitate 24 hrs prior to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), and were sacrificed 24 hrs later, one hr after an intraperitoneal injection of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU). Sera were analyzed for TNFalpha and IL-1beta. Liver sections were stained immunohistochemically and quantified for BrdU incorporated into DNA.
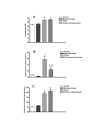
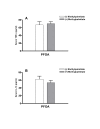
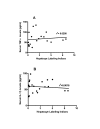
Results: Data show that PFOA remarkably stimulated hepatocellular proliferation in the absence of significant changes in the serum levels of either TNFalpha or IL-1beta. In addition, methylpalmitate did not alter the levels of these mitogens in PFOA-treated animals, despite the fact that it significantly blocked the hepatocellular proliferative effect of PFOA. Correlation between hepatocellular proliferation and serum levels of TNFalpha or IL-1beta was extremely poor.
Conclusion: It is unlikely that mechanisms involving Kupffer cells play an eminent role in the hepatic hyperplasia, and consequently hepatocarcinogenicity attributed to PPARalpha agonists. This conclusion is based on the above mentioned published data and the current findings showing animals treated with PFOA alone or in combination with methylpalmitate to have similar levels of serum TNFalpha and IL-1beta, which are reliable indicators of Kupffer cell activity, despite a remarkable difference in hepatocellular proliferation.
Figures
References
-
- Reddy JK. Carcinogenecity of peroxisome proliferators: evaluation and mechanisms. Biochem Soc Trans. 1999;18:92–94. - PubMed
-
- Marsman DS, Cattley RC, Conway JG, Popp JA. Relationship of hepatic peroxisome proliferation and replicative DNA synthesis to the hepatocarcinogenicity of the peroxisome proliferators di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and [4-Chloro-6-(2,3-xylidino))-2-pyrimidinylthio]acetic acid (Wy-14,643) in rats. Cancer Res. 1988;48:6739–6744. - PubMed
-
- Soliman M, Cunningham M, Morrow J, Roberts LJ, Badr M. Evidence against peroxisome proliferation-induced hepatic oxidative damage. Levels of esterified isoprostanes in livers of mice fed a diet containing [4-chloro-6-(2,3-xylidino)-2pyrimidinylthio]acetic acid (Wy-14,643) Biochem Pharmacol. 1997;53:1369–1374. doi: 10.1016/S0006-2952(97)87956-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bojes HK, Germolec DR, Simeonova P, Bruccoleri A, Schoonhiven R, Luster MI, Thurman RG. Antibodies to tumor necrosis factor α prevent increases in cell replication in liver due to the potent peroxisome proliferator, Wy-14,643. Carcinogenesis. 1997;18:669–674. doi: 10.1093/carcin/18.4.669. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

