Delta and theta oscillations as risk markers in adolescent offspring of alcoholics
- PMID: 17129626
- PMCID: PMC2020838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2006.10.003
Delta and theta oscillations as risk markers in adolescent offspring of alcoholics
Abstract
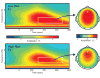
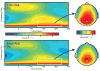
Background: Visual P300 is consistently lower in alcohol-dependent individuals, their offspring and subjects at risk. Delta and theta event-related oscillations (ERO) are the major contributors to the P300 signal. The total and evoked power in delta and theta bands in the 300 to 700 ms post-stimulus window (corresponding to the zone of P300 maxima) was compared between adolescent offspring of alcoholics (high-risk) and age-matched normal controls (low-risk), to assess the utility of the risk markers.
Methods: EEG was recorded during the performance of a visual oddball task. The S-transform algorithm decomposed the EEG signals into different frequency bands and the group differences in total and evoked power in the oscillatory responses during the P300 time window (300 to 700 ms) were analyzed using a multivariate design. Similar analysis was performed on P300 peak amplitude for the target.
Results: The high-risk group showed significantly lower parietal post-stimulus evoked and total power in the delta band for targets. A decrease in total power was seen centrally and parietally in the theta band. The P300 peak amplitude in the parietal electrodes was also significantly lower in the high-risk group.
Conclusions: The decreased total theta power and total and evoked delta power for visual targets in high risk individuals may serve as an endophenotypic marker in the development of alcoholism and other disinhibitory disorders. The differences seen between the offspring of alcoholics and controls may have a cholinergic basis. The ERO measures appear to be more robust than the P300 amplitude in differentiating the groups.
Figures
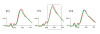
Similar articles
-
Event-related oscillations in offspring of alcoholics: neurocognitive disinhibition as a risk for alcoholism.Biol Psychiatry. 2006 Apr 1;59(7):625-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.08.017. Epub 2005 Oct 6. Biol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16213472 Free PMC article.
-
Event-related oscillations versus event-related potentials in a P300 task as biomarkers for alcoholism.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010 Apr;34(4):669-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01136.x. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010. PMID: 20102573 Free PMC article.
-
S-transform time-frequency analysis of P300 reveals deficits in individuals diagnosed with alcoholism.Clin Neurophysiol. 2006 Oct;117(10):2128-43. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2006.02.028. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Clin Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16926113
-
Children of alcoholics: attention, information processing and event-related brain potentials.Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1994 Nov;404:4-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb13375.x. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1994. PMID: 7841634 Review.
-
P300-response: possible psychophysiological correlates in delta and theta frequency channels. A review.Int J Psychophysiol. 1992 Sep;13(2):161-79. doi: 10.1016/0167-8760(92)90055-g. Int J Psychophysiol. 1992. PMID: 1399755 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Electrophysiological Research.Alcohol Res. 2015;37(1):53-87. Alcohol Res. 2015. PMID: 26259089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The collaborative study on the genetics of alcoholism: Brain function.Genes Brain Behav. 2023 Oct;22(5):e12862. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12862. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Genes Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37587903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic correlates of the development of theta event related oscillations in adolescents and young adults.Int J Psychophysiol. 2017 May;115:24-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Int J Psychophysiol. 2017. PMID: 27847216 Free PMC article.
-
Theta oscillations during the processing of monetary loss and gain: a perspective on gender and impulsivity.Brain Res. 2008 Oct 15;1235:45-62. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.06.051. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18616934 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic alcohol neuroadaptation and stress contribute to susceptibility for alcohol craving and relapse.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Feb;129(2):149-71. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.09.007. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 20951730 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agrawal A, Edenberg HJ, Foroud T, Bierut LJ, Dunne G, Hinrichs AL, Nurnberger JI, Crowe R, Kuperman S, Schuckit MA, Begleiter H, Porjesz B, Dick DM. Association of GABRA2 with Drug Dependence in the Collaborative Study of the Genetics of Alcoholism Sample. Behav Genet 2006 - PubMed
-
- Alcantara AA, Mrzljak L, Jakab RL, Levey AI, Hersch SM, Goldman-Rakic PS. Muscarinic m1 and m2 receptor proteins in local circuit and projection neurons of the primate striatum: anatomical evidence for cholinergic modulation of glutamatergic prefronto-striatal pathways. J Comp Neurol. 2001;434:445–60. - PubMed
-
- Basar-Eroglu C, Basar E. A compound P300-40 Hz response of the cat hippocampus. Int J Neurosci. 1991;60:227–37. - PubMed
-
- Basar-Eroglu C, Basar E, Demiralp T, Schurmann M. P300-response: possible psychophysiological correlates in delta and theta frequency channels. A review. Int J Psychophysiol. 1992;13:161–79. - PubMed
-
- Basar-Eroglu C, Demiralp T. Event-related theta oscillations: an integrative and comparative approach in the human and animal brain. Int J Psychophysiol. 2001;39:167–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

