CoMoDis: composite motif discovery in mammalian genomes
- PMID: 17130158
- PMCID: PMC1702496
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl839
CoMoDis: composite motif discovery in mammalian genomes
Abstract
Specificity of mammalian gene regulatory regions is achieved to a large extent through the combinatorial binding of sets of transcription factors to distinct binding sites, discrete combinations of which are often referred to as regulatory modules. Identification and subsequent characterization of gene regulatory modules will be a key step in assembling transcriptional regulatory networks from gene expression profiling data, with the ultimate goal of unravelling the regulatory codes that govern gene expression in various cell types. Here we describe the new bioinformatics tool, Composite Motif Discovery (CoMoDis), which streamlines computational identification of novel regulatory modules starting from a single seed motif. Seed motifs represent binding sites conserved across mammalian species. CoMoDis facilitates novel motif discovery by automating the extraction of DNA sequences flanking seed motifs and streamlining downstream motif discovery using a variety of tools, including several that utilize phylogenetic conservation criteria. CoMoDis is available at http://hscl.cimr.cam.ac.uk/CoMoDis_portal.html.
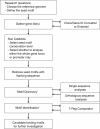
Figures
Similar articles
-
TFBScluster web server for the identification of mammalian composite regulatory elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W524-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl041. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845063 Free PMC article.
-
CompMoby: comparative MobyDick for detection of cis-regulatory motifs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Oct 27;9:455. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-455. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18950538 Free PMC article.
-
MoD Tools: regulatory motif discovery in nucleotide sequences from co-regulated or homologous genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W566-70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl285. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845071 Free PMC article.
-
Computational identification of transcriptional regulatory elements in DNA sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 19;34(12):3585-98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl372. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16855295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational biology: toward deciphering gene regulatory information in mammalian genomes.Biometrics. 2006 Sep;62(3):645-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-0420.2006.00625.x. Biometrics. 2006. PMID: 16984301 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factor site dependencies in human, mouse and rat genomes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 16;10:339. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-339. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19835596 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating sequence, evolution and functional genomics in regulatory genomics.Genome Biol. 2009;10(1):202. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-1-202. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Genome Biol. 2009. PMID: 19226437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MOPAT: a graph-based method to predict recurrent cis-regulatory modules from known motifs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Aug;36(13):4488-97. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn407. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18606616 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the NOD/SCID xenograft model for glucocorticoid-regulated gene expression in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.BMC Genomics. 2011 Nov 17;12:565. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-565. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22093874 Free PMC article.
-
A Runx1-Smad6 rheostat controls Runx1 activity during embryonic hematopoiesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul;31(14):2817-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01305-10. Epub 2011 May 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21576367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nobrega M.A., Ovcharenko I., Afzal V., Rubin E.M. Scanning human gene deserts for long-range enhancers. Science. 2003;302:413. - PubMed
-
- Blanchette M., Bataille A.R., Chen X., Poitras C., Laganiere J., Lefebvre C., Deblois G., Giguere V., Ferretti V., Bergeron D., et al. Genome-wide computational prediction of transcriptional regulatory modules reveals new insights into human gene expression. Genome. Res. 2006;16:656–668. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Donaldson I.J., Chapman M., Gottgens B. TFBScluster: a resource for the characterization of transcriptional regulatory networks. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3058–3059. - PubMed

