Insulin resistance and hepatitis C
- PMID: 17131467
- PMCID: PMC4087766
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7075
Insulin resistance and hepatitis C
Abstract
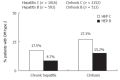
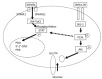
Insulin resistance is the major feature of the metabolic syndrome and depends on insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity. In chronic hepatitis C, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus are more often seen than in healthy controls or chronic hepatitis B patients. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection promotes insulin resistance, mainly by increased TNF production together with enhancement of suppressor of cytokine (SOC-3); both events block PI3K and Akt phosphorylation. Two types of insulin resistance could be found in chronic hepatitis C patients: "viral" and "metabolic" insulin resistance. Insulin resistance in chronic hepatitis C is relevant because it promotes steatosis and fibrosis. The mechanisms by which insulin resistance promotes fibrosis progression include: (1) steatosis, (2) hyperleptinemia, (3) increased TNF production, (4) impaired expression of PPARgamma receptors. Lastly, insulin resistance has been found as a common denominator in patients difficult-to-treat like cirrhotics, overweight, HIV coinfected and Afro-American. Insulin resistance together with fibrosis and genotype has been found to be independently associated with impaired response rate to peginterferon plus ribavirin. Indeed, in genotype 1, the sustained response rate was twice (60%) in patients with HOMA < or = 2 than patients with HOMA > 2. In experiments carried out on Huh-7 cells transfected by full length HCVRNA, interferon alpha blocks HCV replication. However, when insulin (at doses of 128 microU/mL, similar that seen in the hyperinsulinemic state) was added to interferon, the ability to block HCV replication disappeared, and the PKR synthesis was abolished. In summary, hepatitis C promotes insulin resistance and insulin resistance induces interferon resistance, steatosis and fibrosis progression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis: insulin resistance and sustained virological response in hepatitis C.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Aug;34(3):297-305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04716.x. Epub 2011 May 29. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21623851
-
Role of insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in the progression of fibrosis and response to treatment in hepatitis C.Liver Int. 2011 Jan;31 Suppl 1:23-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02397.x. Liver Int. 2011. PMID: 21205134
-
Insulin resistance predicts response to peginterferon-alpha/ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients.J Hepatol. 2009 Apr;50(4):712-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.12.017. Epub 2009 Feb 6. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19231011
-
Hepatitis C and insulin resistance: steatosis, fibrosis and non-response.Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2006 Aug;98(8):605-15. doi: 10.4321/s1130-01082006000800006. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2006. PMID: 17048997 Review. English, Spanish.
-
[Insulin resistance in chronic hepatitits C].Arq Gastroenterol. 2007 Apr-Jun;44(2):178-84. doi: 10.1590/s0004-28032007000200017. Arq Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17962866 Review. Portuguese.
Cited by
-
A lower serum gamma-glutamyltransferase level does not predict a sustained virological response in patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1.Gut Liver. 2013 Jan;7(1):74-81. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2013.7.1.74. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Gut Liver. 2013. PMID: 23423958 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus, Insulin Resistance, and Steatosis.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2016 Mar 28;4(1):66-75. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2015.00051. Epub 2016 Mar 15. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27047774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Algerian patients with hepatitis C virus infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Jul 21;16(27):3427-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i27.3427. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20632447 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic steatosis in HCV-infected persons in the direct-acting antiviral era.Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2016 Sep 27;2:21. doi: 10.1186/s40794-016-0038-5. eCollection 2016. Trop Dis Travel Med Vaccines. 2016. PMID: 28883965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of hepatitis C virus with insulin resistance: evidences from animal studies and clinical studies.Hepat Mon. 2012 Jan;12(1):11-5. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Hepat Mon. 2012. PMID: 22451839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet. 2005;365:1415–1428. - PubMed
-
- Kruszynska YT, Home PD, McIntyre N. Relationship between insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1991;14:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Narita R, Abe S, Kihara Y, Akiyama T, Tabaru A, Otsuki M. Insulin resistance and insulin secretion in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2004;41:132–138. - PubMed
-
- Hui JM, Sud A, Farrell GC, Bandara P, Byth K, Kench JG, McCaughan GW, George J. Insulin resistance is associated with chronic hepatitis C virus infection and fibrosis progression [corrected] Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1695–1704. - PubMed
-
- Lecube A, Hernández C, Genescà J, Simó R. Proinflammatory cytokines, insulin resistance, and insulin secretion in chronic hepatitis C patients: A case-control study. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1096–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

