OPC-67683, a nitro-dihydro-imidazooxazole derivative with promising action against tuberculosis in vitro and in mice
- PMID: 17132069
- PMCID: PMC1664607
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030466
OPC-67683, a nitro-dihydro-imidazooxazole derivative with promising action against tuberculosis in vitro and in mice
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) is still a leading cause of death worldwide. Almost a third of the world's population is infected with TB bacilli, and each year approximately 8 million people develop active TB and 2 million die as a result. Today's TB treatment, which dates back to the 1970s, is long and burdensome, requiring at least 6 mo of multidrug chemotherapy. The situation is further compounded by the emergence of multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) and by the infection's lethal synergy with HIV/AIDS. Global health and philanthropic organizations are now pleading for new drug interventions that can address these unmet needs in TB treatment.
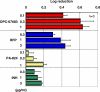
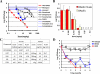
Methods and findings: Here we report OPC-67683, a nitro-dihydro-imidazooxazole derivative that was screened to help combat the unmet needs in TB treatment. The compound is a mycolic acid biosynthesis inhibitor found to be free of mutagenicity and to possess highly potent activity against TB, including MDR-TB, as shown by its exceptionally low minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) range of 0.006-0.024 microg/ml in vitro and highly effective therapeutic activity at low doses in vivo. Additionally, the results of the post-antibiotic effect of OPC-67683 on intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis showed the agent to be highly and dose-dependently active also against intracellular M. tuberculosis H37Rv after a 4-h pulsed exposure, and this activity at a concentration of 0.1 microg/ml was similar to that of the first-line drug rifampicin (RFP) at a concentration of 3 microg/ml. The combination of OPC-67683 with RFP and pyrazinamide (PZA) exhibited a remarkably quicker eradication (by at least 2 mo) of viable TB bacilli in the lung in comparison with the standard regimen consisting of RFP, isoniazid (INH), ethambutol (EB), and PZA. Furthermore, OPC-67683 was not affected by nor did it affect the activity of liver microsome enzymes, suggesting the possibility for OPC-67683 to be used in combination with drugs, including anti-retrovirals, that induce or are metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Conclusions: We concluded that based on these properties OPC-67683 has the potential to be used as a TB drug to help combat the unmet needs in TB treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Removing obstacles to healthy development. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1999.
-
- Dye C, Scheele S, Dolin P, Pathania V, Raviglione MC. Consensus statement. Global burden of tuberculosis: Estimated incidence, prevalence, and mortality by country. WHO Global Surveillance and Monitoring Project. JAMA. 1999;282:677–686. - PubMed
-
- Espinal MA. The global situation of MDR-TB. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2003;83:44–51. - PubMed
-
- Farmer PE, Kononets AS, Borisov SE, Goldfarb A, Healing T, et al. Recrudescent tuberculosis in the Russian Federation. In: Farmer PE, Reichman LB, Iseman MD, editors. The global impact of drug resistant tuberculosis. Boston (Massachusetts): Harvard Medical School/Open Society Institute; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

