Real-time fMRI using brain-state classification
- PMID: 17133383
- PMCID: PMC6871430
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20326
Real-time fMRI using brain-state classification
Abstract
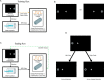
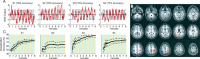
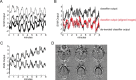
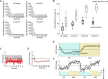
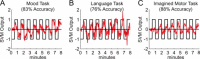
We have implemented a real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging system based on multivariate classification. This approach is distinctly different from spatially localized real-time implementations, since it does not require prior assumptions about functional localization and individual performance strategies, and has the ability to provide feedback based on intuitive translations of brain state rather than localized fluctuations. Thus this approach provides the capability for a new class of experimental designs in which real-time feedback control of the stimulus is possible-rather than using a fixed paradigm, experiments can adaptively evolve as subjects receive brain-state feedback. In this report, we describe our implementation and characterize its performance capabilities. We observed approximately 80% classification accuracy using whole brain, block-design, motor data. Within both left and right motor task conditions, important differences exist between the initial transient period produced by task switching (changing between rapid left or right index finger button presses) and the subsequent stable period during sustained activity. Further analysis revealed that very high accuracy is achievable during stable task periods, and that the responsiveness of the classifier to changes in task condition can be much faster than signal time-to-peak rates. Finally, we demonstrate the versatility of this implementation with respect to behavioral task, suggesting that our results are applicable across a spectrum of cognitive domains. Beyond basic research, this technology can complement electroencephalography-based brain computer interface research, and has potential applications in the areas of biofeedback rehabilitation, lie detection, learning studies, virtual reality-based training, and enhanced conscious awareness.
Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Chen W, Zhu XH, Kato T, Andersen P, Ugurbil K ( 1998): Spatial and temporal differentiation of fMRI BOLD response in primary visual cortex of human brain during sustained visual simulation. Magn Reson Med 39: 520–527. - PubMed
-
- Cherkassky V, Mulier F ( 1998): Learning From Data: Concepts, Theory, and Methods. New York: Wiley.
-
- Collobert R, Weston J, Bottou L ( 2006): Trading convexity for scalability. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning,Pittsburgh, PA.
-
- Cox DD, Savoy RL ( 2003): Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) “brain reading:” detecting and classifying distributed patterns of fMRI activity in human visual cortex. Neuroimage 19: 261–270. - PubMed
-
- Cox RW ( 1996): AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput Biomed Res 29: 162–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

