AnimalQTLdb: a livestock QTL database tool set for positional QTL information mining and beyond
- PMID: 17135205
- PMCID: PMC1781224
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl946
AnimalQTLdb: a livestock QTL database tool set for positional QTL information mining and beyond
Abstract
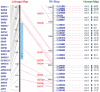
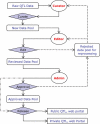
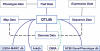
The Animal Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) database (AnimalQTLdb) is designed to house all publicly available QTL data on livestock animal species from which researchers can easily locate and compare QTL within species. The database tools are also added to link the QTL data to other types of genomic information, such as radiation hybrid (RH) maps, finger printed contig (FPC) physical maps, linkage maps and comparative maps to the human genome, etc. Currently, this database contains data on 1287 pig, 630 cattle and 657 chicken QTL, which are dynamically linked to respective RH, FPC and human comparative maps. We plan to apply the tool to other animal species, and add more structural genome information for alignment, in an attempt to aid comparative structural genome studies (http://www.animalgenome.org/QTLdb/).
Figures


References
-
- Womack J.E. Advances in livestock genomics: Opening the barn door. Genome Res. 2005;15:1699–1705. - PubMed
-
- Korstanje R., Paigen B. From QTL to gene: The harvest begins. Nature Genet. 2002;31:235–236. - PubMed
-
- Sawkins M.C., Farmer A.D., Hoisington D., Sullivan J., Tolopko A., Jiang Z., Ribaut J.M. Comparative Map and Trait Viewer (CMTV): an integrated bioinformatic tool to construct consensus maps and compare QTL and functional genomics data across genomes and experiments. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004;56:465–480. - PubMed
-
- Hu Z.-L., Dracheva S., Jang W.-H., Maglott D., Bastiaansen J., Rothschild M.F., Reecy J.M. A QTL resource and comparison tool for pigs: PigQTLDB. Mamm. Genome. 2005;16:792–800. - PubMed
-
- Meyers S.N., Rogatcheva M.B., Larkin D.M., Yerle M., Milan D., Hawken R.J., Schook L.B., Beever J.E. Piggy-BACing the human genome II. A high-resolution, physically anchored, comparative map of the porcine autosomes. Genomics. 2005;86:739–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

