Temperate bacteriophages affect pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns of Campylobacter jejuni
- PMID: 17135440
- PMCID: PMC1829001
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01513-06
Temperate bacteriophages affect pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns of Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
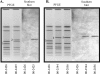
The recently sequenced genome of Campylobacter jejuni RM1221 revealed the presence of three integrated bacteriophage-like elements. In this study, genes from the first element, a Mu-like bacteriophage, were amplified by PCR and used to probe pulsed-field gels of clinical C. jejuni strains obtained from a waterborne outbreak (Ontario, Canada, 2000). These highly similar strains differed only by their pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) patterns due to an apparent insertion or deletion of a 40-kb fragment. Bacteriophage probes hybridized to these different bands in Southern blot analysis, indicating that homologues of bacteriophage genes were present in the outbreak strains. Investigation of the bacteriophage insertion sites in these isolates suggested that bacteriophage acquisition, loss, or transposition was responsible for the PFGE pattern variation. The bacteriophage gene sequences were similar, but not identical, in the outbreak strains and RM1221, indicating that differences may exist between the bacteriophages.
Figures

References
-
- Clark, C. G., L. Bryden, W. R. Cuff, P. L. Johnson, F. Jamieson, B. Ciebin, and G. Wang. 2005. Use of the Oxford multilocus sequence typing protocol and sequencing of the flagellin short variable region to characterize isolates from a large outbreak of waterborne Campylobacter sp. strains in Walkerton, Ontario, Canada. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43:2080-2091. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

