Evaluation of an indirect immunofluorescence assay for strongyloidiasis as a tool for diagnosis and follow-up
- PMID: 17135451
- PMCID: PMC1797793
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00278-06
Evaluation of an indirect immunofluorescence assay for strongyloidiasis as a tool for diagnosis and follow-up
Abstract
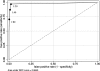
The diagnostic accuracy of an indirect immunofluorescence antibody test (IFAT) for Strongyloides stercoralis at different serum antibody titers was evaluated. To assess diagnostic sensitivity, sera from 156 patients with known strongyloidiasis were collected. Negative control sera were obtained from a composite group of 427 subjects (blood donors and hospitalized patients). With an area under the receiver-operating characteristic plot of 0.98, the IFAT showed a high level of diagnostic accuracy for strongyloidiasis. An antibody titer of > or = 1:20, with 97% sensitivity and 98% specificity, was identified as the diagnostic threshold with the best overall performance. Cross-reactions were evaluated with 41 additional samples from patients with other known helminth infections, and the IFAT detected low-titer positivity in only one subject with filariasis. A positive IFAT result at an antibody dilution of > or = 1:80 was virtually 100% specific, with 71% sensitivity. To test the usefulness of the IFAT as a monitoring tool, the changes in specific-antibody titers after treatment in a group of 155 patients were evaluated. Seroreversion or a decrease in antibody titer of twofold or more was observed in 60% of the patients. Response to treatment was directly correlated to the initial antibody titer, and a baseline titer of > or = 1:80 was identified as the best predictor of response. In conclusion, a positive IFAT result at an antibody dilution of >/=1:20 is the optimal cutoff for screening. A titer of > or = 1:80, with virtually no false-positive result, is a reliable cutoff for a serological assessment of treatment efficacy and for inclusion in clinical trials.
Figures
References
-
- Adams, M., W. Page, and R. Speare. 14. March 2003, posting date. Strongyloidiasis: an issue in Aboriginal communities. Rural Remote Health 3:152. http://rrh.deakin.edu.au. - PubMed
-
- Adenusi, A. A., A. O. Oke, and A. O. Adenusi. 2003. Comparison of ivermectin and thiabendazole in the treatment of uncomplicated human Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2:465-469.
-
- Alcaraz, C. O., R. I. Adell, P. S. Sanchez, M. J. Blasco, O. A. Sanchez, A. S. Aunon, and D. R. Calabuig. 2004. Characteristics and geographical profile of strongyloidiasis in healthcare area 11 of the Valencian community (Spain). J. Infect. 49:152-158. - PubMed
-
- Blatt, J. M., and G. A. Cantos. 2003. Evaluation of techniques for the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive and HIV negative individuals in the city of Itajai, Brazil. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 7:402-408. - PubMed
-
- Bourée, P. 1987. Examens de laboratoire en médecine tropicale, p. 87-88. Masson, Paris, France.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources