S100 chemokines mediate bookmarking of premetastatic niches
- PMID: 17139281
- PMCID: PMC2955889
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1206-1321
S100 chemokines mediate bookmarking of premetastatic niches
Abstract
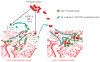
Primary tumours release soluble factors, including VEGF-A, TGFβ and TNFα, which induce expression of the chemokines S100A8 and S100A9 in the myeloid and endothelial cells within the lung before tumour metastasis. These chemokine-activated premetastatic niches support adhesion and invasion of disseminating malignant cells, thereby establishing a fertile habitat for metastatic tumours.
Figures
Comment on
-
Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis.Nat Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;8(12):1369-75. doi: 10.1038/ncb1507. Epub 2006 Nov 26. Nat Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17128264
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

