Pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies of a bone-targeting drug delivery system based on N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymers
- PMID: 17140259
- PMCID: PMC2504859
- DOI: 10.1021/mp0600539
Pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies of a bone-targeting drug delivery system based on N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymers
Abstract
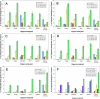
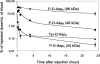
Osteotropicity of novel bone-targeted HPMA copolymer conjugates has been demonstrated previously with bone histomorphometric analysis. The pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of this delivery system were investigated in the current study with healthy young BALB/c mice. The 125I-labeled bone-targeted and control (nontargeted) HPMA copolymers were administered intravenously to mice, and their distribution to different organs and tissues was followed using gamma counter and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). Both the invasive and noninvasive data further confirmed that the incorporation of D-aspartic acid octapeptide (D-Asp8) as bone-targeting moiety could favorably deposit the HPMA copolymers to the entire skeleton, especially to the high bone turnover sites. To evaluate the influence of molecular weight, three fractions (Mw of 24, 46, and 96 kDa) of HPMA copolymer-D-Asp8 conjugate were prepared and evaluated. Higher molecular weight of the conjugate enhanced the deposition to bone due to the prolonged half-life in circulation, but it weakened the bone selectivity. A higher content of bone-targeting moiety (D-Asp8) in the conjugate is desirable to achieve superior hard tissue selectivity. Further validation of the bone-targeting efficacy of the conjugates in animal models of osteoporosis and other skeletal diseases is needed in the future.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biodistribution and pharmacokinetic studies of bone-targeting N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymer-alendronate conjugates.Mol Pharm. 2008 Jul-Aug;5(4):548-58. doi: 10.1021/mp800003u. Epub 2008 May 28. Mol Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18505266 Free PMC article.
-
Star structure of antibody-targeted HPMA copolymer-bound doxorubicin: a novel type of polymeric conjugate for targeted drug delivery with potent antitumor effect.Bioconjug Chem. 2002 Mar-Apr;13(2):206-15. doi: 10.1021/bc010063m. Bioconjug Chem. 2002. PMID: 11906257
-
Noninvasive visualization of pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and tumor targeting of poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide] in mice using contrast enhanced MRI.Pharm Res. 2007 Jun;24(6):1208-16. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9252-1. Epub 2007 Mar 27. Pharm Res. 2007. PMID: 17387601
-
Molecular imaging of HPMA copolymers: visualizing drug delivery in cell, mouse and man.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Feb 17;62(2):246-57. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.12.007. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 20060431 Review.
-
HPMA Copolymers: A Versatile Platform for Targeted Peptide Drug Delivery.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 17;15(4):596. doi: 10.3390/biom15040596. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Real-World Methotrexate Dose on Clinical Effectiveness and Structural Damage of Certolizumab Pegol With Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Apr 21;8:643459. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.643459. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33968956 Free PMC article.
-
Bone-Targeting Systems to Systemically Deliver Therapeutics to Bone Fractures for Accelerated Healing.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020 Oct;18(5):449-459. doi: 10.1007/s11914-020-00604-4. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020. PMID: 32860563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPMA copolymers: origins, early developments, present, and future.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Feb 17;62(2):122-49. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.10.004. Epub 2009 Nov 14. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 19919846 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced affinity bifunctional bisphosphonates for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents to bone.Bioconjug Chem. 2011 Dec 21;22(12):2496-506. doi: 10.1021/bc2003132. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Bioconjug Chem. 2011. PMID: 22073906 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting polymer therapeutics to bone.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012 Sep;64(12):1189-204. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.01.012. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012. PMID: 22316530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burckhardt P, Christiansen C, Fleisch HA. Consensus Development Conference: Prophylaxis and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Am. J. Med. 1991;90:107–110. - PubMed
-
- National Osteoporosis Foundation America's Bone Health: The State of Osteoporosis and Low Bone Mass in Our Nation. 2002. pp. 1–16.
-
- O'Dell JR. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2591–2602. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS. Etiology and Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. In: Harris ED Jr., Budd RC, Genovese MC, Firestein GS, Sargent JS, Sledge CB, editors. Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 7th ed. Elsevier Saunders; Philadelphia: 2005. p. 996.
-
- Wieland HA, Michaelis M, Kirschbaum BJ, Rudolphi KA. Osteoarthritis - an untreatable disease? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4:331–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

