Adiponectin actions in the cardiovascular system
- PMID: 17140553
- PMCID: PMC1858678
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.10.009
Adiponectin actions in the cardiovascular system
Abstract
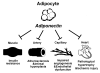
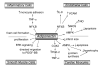
Obesity is strongly associated with the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Levels of the hormone adiponectin are downregulated in obese individuals, and several experimental studies show that adiponectin protects against the development of various obesity-related metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Adiponectin exhibits favorable effects on atherogenesis, endothelial function, and vascular remodeling by modulation of signaling cascades in cells of the vasculature. More recent findings have shown that adiponectin directly affects signaling in cardiac cells and is beneficial in the setting of pathological cardiac remodeling and acute cardiac injury. Several of these effects of adiponectin have been attributed to the activation of the 5' AMP-activated protein kinase signaling cascade and other signaling proteins. This review will discuss the epidemiological and experimental studies that have elucidated the role of adiponectin in a variety of cardiovascular diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin and interleukin-6 in inflammation-associated disease.Vitam Horm. 2012;90:375-95. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-398313-8.00014-2. Vitam Horm. 2012. PMID: 23017723 Review.
-
Adiponectin and cardiovascular disease.Circ J. 2009 Apr;73(4):608-14. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-09-0057. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Circ J. 2009. PMID: 19261992 Review.
-
Cardioprotection by adiponectin.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2006 Jul;16(5):141-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2006.03.001. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2006. PMID: 16781946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
-
Adiponectin and hypertension.Am J Hypertens. 2011 Mar;24(3):263-9. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2010.216. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Am J Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 20930707 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Pre-Clinical Development of Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Therapies for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 25;12(7):1407. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071407. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Adiponectin and Indices of Cardiovascular Risk in Young Women with Excessive Body Mass.EJIFCC. 2010 Oct 29;21(3):68-73. eCollection 2010 Oct. EJIFCC. 2010. PMID: 27683376 Free PMC article.
-
276G>T Polymorphism of the ADIPOQ Gene Influences Plasma Adiponectin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients but Is Not Predictive for Presence of Type 2 Diabetes in a Caucasian Cohort from Romania.Maedica (Bucur). 2012 Dec;7(4):271-6. Maedica (Bucur). 2012. PMID: 23483234 Free PMC article.
-
High fat diet enhances cardiac abnormalities in SHR rats: Protective role of heme oxygenase-adiponectin axis.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2011 Dec 23;3(1):37. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-3-37. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2011. PMID: 22196253 Free PMC article.
-
Serum adipokine concentrations in dogs with naturally occurring pituitary-dependent hyperadrenocorticism.J Vet Intern Med. 2014 Mar-Apr;28(2):429-36. doi: 10.1111/jvim.12270. Epub 2013 Dec 26. J Vet Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24372863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg AH, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2005;96:939–49. - PubMed
-
- Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2005;436:356–62. - PubMed
-
- Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:10697–703. - PubMed
-
- Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1) Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;221:286–9. - PubMed
-
- Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:26746–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

