Long survival in rats after multivisceral versus isolated small-bowel allotransplantation under FK 506
- PMID: 1714104
- PMCID: PMC2975982
Long survival in rats after multivisceral versus isolated small-bowel allotransplantation under FK 506
Abstract
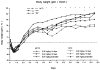
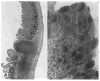
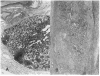
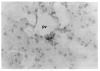
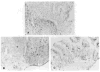
Abdominal multivisceral allotransplantation (MVTX) from Brown Norway donor rats to Lewis recipient rats was performed under a 14-day course of low (0.32 mg/kg) or high-dose (0.64 mg/kg) intramuscular FK 506 to which weekly further injections were added in some of the high-dose animals. With all three regimens, long survival was frequently achieved with good intestinal adsorption and weight gain, but histopathologic evidence of intestinal rejection existed in the most lightly treated animals. The liver, stomach, and pancreas had only minor abnormalities. Rejection of isolated intestinal grafts was more difficult to control based on histopathologic criteria, and satisfactory results were obtained only with the most aggressive treatment protocol, suggesting that the liver in the MVTX had provided an advantage to the companion organs of the graft, of which the intestine was most vulnerable. Histopathologically, the lymphoid elements of the intestine, including the Peyer's patches, appeared to be the most immunogenic component of the intestine. Epithelium near lymphoid areas was secondarily involved with villous atrophy, cryptitis, and abscess formation. Beginning within 12 days in successful MVTX experiments, the lymphoreticular components of the graft intestine, including the Peyer's patches, lamina propria, and mesenteric nodes, were shown with anti-Ia monoclonal antibodies to be repopulated with recipient cells. This finding in grafts that appeared to be permanently accepted was surprising and contrary to expectations from the literature on intestinal allotransplantation.
Figures



References
-
- Williams JW, Sankary HN, Foster P, Lowe J, Goldman GM. Splanchnic transplantation: an approach to the infant dependent on parenteral nutrition who develops irreversible liver disease. JAMA. 1989;261:1458–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
