Knockdown of Nurr1 in the rat hippocampus: implications to spatial discrimination learning and memory
- PMID: 17142303
- PMCID: PMC1783627
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.407706
Knockdown of Nurr1 in the rat hippocampus: implications to spatial discrimination learning and memory
Abstract
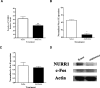
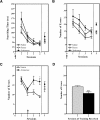
Nurr1 expression is up-regulated in the brain following associative learning experiences, but its relevance to cognitive processes remains unclear. In these studies, rats initially received bilateral hippocampal infusions of control or antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) 1 h prior to training in a holeboard spatial discrimination task. Such pre-training infusions of nurr1 antisense ODNs caused a moderate effect in learning the task and also impaired LTM tested 7 d later. In a second experiment, ODN infusions were given immediately after the animals had received two sessions of training, during which all animals showed normal learning. Although antisense treated rats were significantly impaired during the post-infusion stages of acquisition of the task, no group differences were observed during the LTM test given 7 d later. These animals were subjected 3 d later to reversal training in the same maze in the absence of any additional treatments. Remarkably, rats previously treated with antisense ODNs displayed perseveration: The animals were fixated with the previously learned pattern of baited holes, causing them to be significantly impaired in the extinction of acquired spatial preferences and future learning. We postulate that Nurr1 function in the hippocampus is important for normal cognitive processes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hippocampal expression of the orphan nuclear receptor gene hzf-3/nurr1 during spatial discrimination learning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2000 Sep;74(2):161-78. doi: 10.1006/nlme.1999.3952. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2000. PMID: 10933901
-
Chronic lithium decreases Nurr1 expression in the rat brain and impairs spatial discrimination.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004 Dec;79(4):607-21. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2004.09.015. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2004. PMID: 15582669
-
Functional difference between rat perirhinal cortex and hippocampus in object and place discrimination tasks.Behav Brain Res. 2009 Feb 11;197(2):388-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.10.012. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Behav Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 18984009
-
Rats with hippocampal lesion show impaired learning and memory in the ziggurat task: a new task to evaluate spatial behavior.Behav Brain Res. 2008 May 16;189(1):17-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2007.12.002. Epub 2007 Dec 15. Behav Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18192033
-
The appetitively motivated "cognitive" holeboard: a family of complex spatial discrimination tasks for assessing learning and memory.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012 Jan;36(1):379-403. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.07.008. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012. PMID: 21810442 Review.
Cited by
-
The Critical Role of Nurr1 as a Mediator and Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease-related Pathogenesis.Aging Dis. 2020 May 9;11(3):705-724. doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.0718. eCollection 2020 May. Aging Dis. 2020. PMID: 32489714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of HDAC3-Y298H Point Mutant in Medial Habenula Cholinergic Neurons Has No Effect on Cocaine-Induced Behaviors.eNeuro. 2025 May 14;12(5):ENEURO.0590-24.2025. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0590-24.2025. Print 2025 May. eNeuro. 2025. PMID: 40368589 Free PMC article.
-
Nr4a2 Transcription Factor in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity, Memory and Cognitive Dysfunction: A Perspective Review.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Nov 22;14:786226. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.786226. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34880728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance memory and synaptic plasticity via CREB:CBP-dependent transcriptional activation.J Neurosci. 2007 Jun 6;27(23):6128-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0296-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17553985 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 12;110(7):2647-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1213364110. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23297220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal S. Importance of nucleotide sequence and chemical modifications of antisense oligonucleotides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1999;1489:53–68. - PubMed
-
- Al Banchaabouchi M., de Peña Ortiz S., Menendez R., Ren K., Maldonado-Vlaar C.S. Chronic lithium decreases Nurr1 expression in the rat brain and impairs spatial discrimination. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004;79:607–621. - PubMed
-
- Álvarez-Jaimes L., Betancourt E., Centeno-Gonzalez M., Feliciano-Rivera M.Z., Rodriguez D., de Peña Ortiz S., Maldonado-Vlaar C.S. Spatial learning in rats is impaired by microinfusions of protein kinase C-γ antisense oligodeoxynucleotide within the nucleus accumbens. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2004;81:120–136. - PubMed
-
- Andreasson K.I., Kaufmann W.E. Role of immediate early gene expression in cortical morphogenesis and plasticity. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2002;39:113–137. - PubMed
-
- Antonova E., Sharma T., Morris R., Kumari V. The relationship between brain structure and neurocognition in schizophrenia: A selective review. Schizophr. Res. 2004;70:117–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5 T32 MH18882-16/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015565/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R29 DA11665-05/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 MH18882-17/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH018882/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54-NS39405/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM061151/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- SOGGMO 8102-26S1/PHS HHS/United States
- U54 NS039405/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5P20 RR 15565-02/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NC 5R25GM061151/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5 T32 MH18882-15/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
