Glucose induces MafA expression in pancreatic beta cell lines via the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway
- PMID: 17142462
- PMCID: PMC1904346
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M605064200
Glucose induces MafA expression in pancreatic beta cell lines via the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway
Abstract
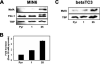
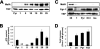
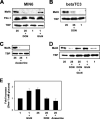
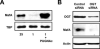
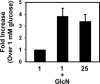
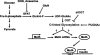
MafA is a basic leucine zipper transcription factor that regulates gene expression in both the neuroretina and pancreas. Within the pancreas, MafA is exclusively expressed in the beta cells and is involved in insulin gene transcription, insulin secretion, and beta cell survival. The expression of the mafA gene within beta cells is known to increase in response to high glucose levels by an unknown mechanism. In this study, we demonstrate that pyruvate, which is produced by glycolysis from glucose, is not sufficient to induce mafA gene expression compared with high glucose. This suggests that the signal for MafA induction is independent of ATP levels and that a metabolic event occurring upstream of pyruvate production leads to the induction of MafA. Furthermore, insulin secretion mediated by high glucose is not important for MafA expression. However, the addition of glucosamine to beta cell lines stimulates MafA expression in the absence of high glucose, and inhibition of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway in the presence of high glucose abolishes MafA induction. Moreover, we demonstrate that the expression of UDP-N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase, the enzyme mediating O-linked glycosylation of cytosolic and nuclear proteins, is essential for glucose-dependent MafA expression. Consistent with this observation, inhibition of N-acetylglucosaminidase, the enzyme involved in the removal of the O-GlcNAc modification from proteins, with O-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d-glucopyranosylidene)amino-N-phenylcarbamate stimulates MafA expression under low glucose conditions. The presented data suggest that MafA expression mediated by high glucose requires flux through the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway and the O-linked glycosylation of an unknown protein(s) by UDP-N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multiple kinases regulate mafA expression in the pancreatic beta cell line MIN6.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008 Dec 15;480(2):138-42. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.10.001. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008. PMID: 18948074 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose mediates the translocation of NeuroD1 by O-linked glycosylation.J Biol Chem. 2007 May 25;282(21):15589-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701762200. Epub 2007 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17403669 Free PMC article.
-
MafA stability in pancreatic beta cells is regulated by glucose and is dependent on its constitutive phosphorylation at multiple sites by glycogen synthase kinase 3.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;27(19):6593-605. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01573-06. Epub 2007 Aug 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17682063 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of β-cell-specific and glucose-dependent MafA expression.Islets. 2011 Jan-Feb;3(1):35-7. doi: 10.4161/isl.3.1.14032. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Islets. 2011. PMID: 21278484 Review.
-
Roles and regulation of transcription factor MafA in islet beta-cells.Endocr J. 2007 Dec;54(5):659-66. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.kr-101. Epub 2007 Aug 30. Endocr J. 2007. PMID: 17785922 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucose activates free fatty acid receptor 1 gene transcription via phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent O-GlcNAcylation of pancreas-duodenum homeobox-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 14;109(7):2376-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1114350109. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22308370 Free PMC article.
-
The hexosamine biosynthesis pathway is essential for pancreatic beta cell development.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24583-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.025288. Epub 2009 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19586915 Free PMC article.
-
Islet beta-cell-specific MafA transcription requires the 5'-flanking conserved region 3 control domain.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;30(17):4234-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01396-09. Epub 2010 Jun 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20584984 Free PMC article.
-
MafA Regulation in β-Cells: From Transcriptional to Post-Translational Mechanisms.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 31;12(4):535. doi: 10.3390/biom12040535. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35454124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of MafA transcriptional activity and human insulin gene transcription by interleukin-1beta and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase in pancreatic islet beta cells.Diabetologia. 2007 Aug;50(8):1678-87. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0712-2. Epub 2007 Jun 22. Diabetologia. 2007. PMID: 17583797
References
-
- LeRoith D. Am. J. Med. 2002;113(Suppl 6A):3–11. - PubMed
-
- Poitout V, Robertson RP. Annu. Rev. Med. 1996;47:69–83. - PubMed
-
- LeRoith D, Taylor SI, Olefsky JM. Diabetes Mellitus: A Fundamental and Clinical Text. 2nd Ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2000.
-
- Nielsen DA, Welsh M, Casadaban MJ, Steiner DF. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:13585–13589. - PubMed
-
- Welsh M, Nielsen DA, MacKrell AJ, Steiner DF. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:13590–13594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

