Molecular regulation of HDL metabolism and function: implications for novel therapies
- PMID: 17143322
- PMCID: PMC1679714
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30163
Molecular regulation of HDL metabolism and function: implications for novel therapies
Abstract
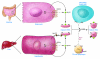
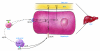
HDL metabolism represents a major target for the development of therapies intended to reduce the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. HDL metabolism is complex and involves dissociation of HDL apolipoprotein and HDL cholesterol metabolism. Advances in our understanding of the molecular regulation of HDL metabolism, macrophage cholesterol efflux, and HDL function will lead to a variety of novel therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Miller G.J., Miller N.E. Plasma-high-density-lipoprotein concentration and development of ischaemic heart-disease. Lancet. 1975;1:16–19. - PubMed
-
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholester ol Education Program (NCEP). JAMA. 2001;285:2486–2497. - PubMed
-
- Lewis G.F., Rader D.J. New insights into the regulation of HDL metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport. Circ. Res. 2005;96:1221–1232. - PubMed
-
- Glomset J.A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J. Lipid Res. 1968;9:155–167. - PubMed
-
- Ross R., Glomset J.A. Atherosclerosis and the arterial smooth muscle cell: proliferation of smooth muscle is a key event in the genesis of the lesions of atherosclerosis. Science. 1973;180:1332–1339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL022633/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL22633/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK06990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL62250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000040/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL055323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK59533/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL70128/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL062250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL55323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00040/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL59407/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL070128/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL059407/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059533/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

