RNAi: a novel strategy for the treatment of prion diseases
- PMID: 17143323
- PMCID: PMC1679715
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30663
RNAi: a novel strategy for the treatment of prion diseases
Abstract
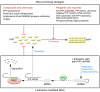
Prion disease refers to a group of fatal transmissible neurodegenerative diseases for which no pharmacological treatment is available. The cellular prion protein (PrP(C)) is required for both prion replication and pathogenesis, and reducing PrP(C) levels has been shown to extend survival time after prion infection. RNA interference (RNAi) is a sequence-specific posttranscriptional gene silencing mechanism. In this issue of the JCI, Pfeifer et al. report that lentivector-mediated RNAi significantly reduced neuronal PrP(C) expression; effectively suppressed accumulation of the infectious protease-resistant form of PrP (PrP(Sc)) in a persistently infected neuroblastoma cell line; and markedly slowed the progression of prion disease in a unique chimeric mouse model (see the related article beginning on page 3204). These findings indicate that lentivector-mediated RNAi could, in principle, be developed for the therapy of prion disease.
Figures
Comment on
-
Lentivector-mediated RNAi efficiently suppresses prion protein and prolongs survival of scrapie-infected mice.J Clin Invest. 2006 Dec;116(12):3204-10. doi: 10.1172/JCI29236. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 17143329 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Lentivector-mediated RNAi efficiently suppresses prion protein and prolongs survival of scrapie-infected mice.J Clin Invest. 2006 Dec;116(12):3204-10. doi: 10.1172/JCI29236. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 17143329 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of RNAi-mediated prnp gene silencing in neuroblastoma cells permanently infected by prions: potentials and limitations.Antiviral Res. 2009 Nov;84(2):185-93. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.09.002. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Antiviral Res. 2009. PMID: 19748523
-
Resistance of cell lines to prion toxicity aided by phospho-ERK expression.J Neurochem. 2008 May;105(3):842-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05192.x. Epub 2007 Dec 15. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18088369
-
Prion encephalopathies of animals and humans.Dev Biol Stand. 1993;80:31-44. Dev Biol Stand. 1993. PMID: 8270114 Review.
-
[Prions and their biology].Rev Neurol. 2000 Jul 16-31;31(2):129-32. Rev Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10951668 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Mouse neuronal cells expressing exogenous bovine PRNP and simultaneous downregulation of endogenous mouse PRNP using siRNAs.Prion. 2010 Jan-Mar;4(1):32-7. doi: 10.4161/pri.4.1.11218. Epub 2010 Jan 15. Prion. 2010. PMID: 20215868 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect and potential of cellular prion protein and its cleavage products for treatment of neurodegenerative disorders part II: strategies for therapeutics development.Expert Rev Neurother. 2021 Sep;21(9):983-991. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2021.1965882. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Expert Rev Neurother. 2021. PMID: 34470554 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Vesicle Trafficking Defects in the Pathogenesis of Prion and Prion-Like Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 23;21(19):7016. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197016. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32977678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New implications for prion diseases therapy and prophylaxis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Mar 4;17:1324702. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1324702. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38500676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective effect and potential of cellular prion protein and its cleavage products for treatment of neurodegenerative disorders part I. a literature review.Expert Rev Neurother. 2021 Sep;21(9):969-982. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2021.1965881. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Expert Rev Neurother. 2021. PMID: 34470561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sailer A., Bueler H., Fischer M., Aguzzi A., Weissmann C. No propagation of prions in mice devoid of PrP. Cell. 1994;77:967–968. - PubMed
-
- Brandner S., et al. Normal host prion protein necessary for scrapie-induced neurotoxicity. Nature. 1996;379:339–343. - PubMed
-
- Aguzzi A., Glatzel M., Montrasio F., Prinz M., Heppner F.L. Interventional strategies against prion diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;2:745–749. - PubMed
-
- Trevitt C.R., Collinge J. A systematic review of prion therapeutics in experimental models. Brain. 2006;129:2241–2265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

