The sticky truth about angiogenesis and thrombospondins
- PMID: 17143327
- PMCID: PMC1678819
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI30685
The sticky truth about angiogenesis and thrombospondins
Abstract
The formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis, is important for embryonic development and wound healing as well as the development of cancer and inflammation; therefore, angiogenesis is a valuable target for clinical intervention. Both logic and empiricism suggest that a balance of stimulatory and inhibitory switches is required for orderly formation of blood vessels. Thrombospondins 1 and 2 were among the first natural angiogenesis inhibitors to be identified. However, the cellular origins and mechanisms of action of these important proteins during angiogenesis have remained largely unknown. Studies by Kopp et al., presented in this issue of the JCI, clarify some of these issues by revealing that megakaryocytes and their "sticky" wound-healing progeny, platelets, are important sources of thrombospondins 1 and 2 and that these thrombopoietic cells play key roles in controlling blood vessel formation during hematopoiesis and ischemic wound healing (see the related article beginning on page 3277).
Figures
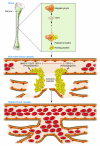
Comment on
-
Thrombospondins deployed by thrombopoietic cells determine angiogenic switch and extent of revascularization.J Clin Invest. 2006 Dec;116(12):3277-91. doi: 10.1172/JCI29314. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 17143334 Free PMC article.

