Myocardial performance in conscious streptozotocin diabetic rats
- PMID: 17144912
- PMCID: PMC1698470
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-5-26
Myocardial performance in conscious streptozotocin diabetic rats
Abstract
Background: In spite of a large amount of studies in anesthetized animals, isolated hearts, and in vitro cardiomyocytes, to our knowledge, myocardial function was never studied in conscious diabetic rats. Myocardial performance and the response to stress caused by dobutamine were examined in conscious rats, fifteen days after the onset of diabetes caused by streptozotocin (STZ). The protective effect of insulin was also investigated in STZ-diabetic rats.
Methods: Cardiac contractility and relaxation were evaluated by means of maximum positive (+dP/dtmax) and negative (-dP/dtmax) values of first derivative of left ventricular pressure over time. In addition, it was examined the myocardial response to stress caused by two dosages (1 and 15 mug/kg) of dobutamine. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare differences among groups, and two-way ANOVA for repeated measure, followed by Tukey post hoc test, to compare the responses to dobutamine. Differences were considered significant if P < 0.05.
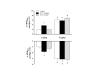
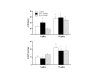
Results: Basal mean arterial pressure, heart rate, +dP/dtmax and -dP/dtmax were found decreased in STZ-diabetic rats, but unaltered in control rats treated with vehicle and STZ-diabetic rats treated with insulin. Therefore, insulin prevented the hemodynamic and myocardial function alterations observed in STZ-diabetic rats. Lower dosage of dobutamine increased heart rate, +dP/dtmax and -dP/dtmax only in STZ-diabetic rats, while the higher dosage promoted greater, but similar, responses in the three groups. In conclusion, the results indicate that myocardial function was remarkably attenuated in conscious STZ-diabetic rats. In addition, the lower dosage of dobutamine uncovered a greater responsiveness of the myocardium of STZ-diabetic rats. Insulin preserved myocardial function and the integrity of the response to dobutamine of STZ-diabetic rats.
Conclusion: The present study provides new data from conscious rats showing that the cardiomyopathy of this pathophysiological condition was expressed by low indices of contractility and relaxation. In addition, it was also demonstrated that these pathophysiological features were prevented by the treatment with insulin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The antiadrenergic effect of cyclopentyladenosine on myocardial contractility is reduced in vivo in diabetic rats.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;72(10):1245-51. doi: 10.1139/y94-177. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7882191
-
Effects of dobutamine and acetylcholine on perfused hearts isolated from streptozocin-induced diabetic rats.Arzneimittelforschung. 1989 Apr;39(4):470-4. Arzneimittelforschung. 1989. PMID: 2751733
-
Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase by L-NAME improves ventricular performance in streptozotocin-diabetic rats.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1997 Sep;29(9):2393-402. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1997.0474. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1997. PMID: 9299363
-
Hemodynamic alterations in chronically conscious unrestrained diabetic rats.Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 2):H900-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.5.H900. Am J Physiol. 1987. PMID: 2953253
-
Glucose-induced metabolic imbalances in the pathogenesis of diabetic vascular disease.Diabetes Metab Rev. 1991 Mar;7(1):35-59. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610070106. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1991. PMID: 1935535 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Chronic Rho-kinase inhibition improves left ventricular contractile dysfunction in early type-1 diabetes by increasing myosin cross-bridge extension.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015 Jul 22;14:92. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0256-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015. PMID: 26194354 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Update: Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus: Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Mechanisms, Management, and Clinical Considerations.Circulation. 2016 Jun 14;133(24):2459-502. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.022194. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 27297342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotective Activity of Pongamia pinnata in Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide Induced Diabetic Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:403291. doi: 10.1155/2015/403291. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25954749 Free PMC article.
-
Altered sympathetic nervous system signaling in the diabetic heart: emerging targets for molecular imaging.Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;2(3):314-34. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 23133819 Free PMC article.
-
Neointimal hyperplasia persists at six months after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation in diabetic porcine.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2007 Jun 5;6:16. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-6-16. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2007. PMID: 17550588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fein FS, Kornstein LB, Strobeck JE, Capasso JM, Sonnenblick EH. Altered myocardial mechanics in diabetic rats. Circ Res. 1980;47:922–933. - PubMed
-
- Ren J, Bode AM. Altered cardiac excitation-contraction coupling in ventricular myocytes from spontaneously diabetic BB rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:H238–H244. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

