Two-temperature LATE-PCR endpoint genotyping
- PMID: 17144924
- PMCID: PMC1698914
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-6-44
Two-temperature LATE-PCR endpoint genotyping
Abstract
Background: In conventional PCR, total amplicon yield becomes independent of starting template number as amplification reaches plateau and varies significantly among replicate reactions. This paper describes a strategy for reconfiguring PCR so that the signal intensity of a single fluorescent detection probe after PCR thermal cycling reflects genomic composition. The resulting method corrects for product yield variations among replicate amplification reactions, permits resolution of homozygous and heterozygous genotypes based on endpoint fluorescence signal intensities, and readily identifies imbalanced allele ratios equivalent to those arising from gene/chromosomal duplications. Furthermore, the use of only a single colored probe for genotyping enhances the multiplex detection capacity of the assay.
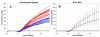
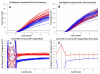
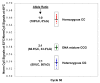
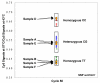
Results: Two-Temperature LATE-PCR endpoint genotyping combines Linear-After-The-Exponential (LATE)-PCR (an advanced form of asymmetric PCR that efficiently generates single-stranded DNA) and mismatch-tolerant probes capable of detecting allele-specific targets at high temperature and total single-stranded amplicons at a lower temperature in the same reaction. The method is demonstrated here for genotyping single-nucleotide alleles of the human HEXA gene responsible for Tay-Sachs disease and for genotyping SNP alleles near the human p53 tumor suppressor gene. In each case, the final probe signals were normalized against total single-stranded DNA generated in the same reaction. Normalization reduces the coefficient of variation among replicates from 17.22% to as little as 2.78% and permits endpoint genotyping with >99.7% accuracy. These assays are robust because they are consistent over a wide range of input DNA concentrations and give the same results regardless of how many cycles of linear amplification have elapsed. The method is also sufficiently powerful to distinguish between samples with a 1:1 ratio of two alleles from samples comprised of 2:1 and 1:2 ratios of the same alleles.
Conclusion: SNP genotyping via Two-Temperature LATE-PCR takes place in a homogeneous closed-tube format and uses a single hybridization probe per SNP site. These assays are convenient, rely on endpoint analysis, improve the options for construction of multiplex assays, and are suitable for SNP genotyping, mutation scanning, and detection of DNA duplication or deletions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PCR amplification on magnetic nanoparticles: application for high-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping.Biotechnol J. 2007 Apr;2(4):508-11. doi: 10.1002/biot.200600214. Biotechnol J. 2007. PMID: 17285677
-
SNP genotyping by unlabeled probe melting analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;429:199-206. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-040-3_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18695968
-
Fluorescent microsphere-based readout technology for multiplexed human single nucleotide polymorphism analysis and bacterial identification.Hum Mutat. 2001 Apr;17(4):305-16. doi: 10.1002/humu.28. Hum Mutat. 2001. PMID: 11295829
-
Duplication and deletion analysis by fluorescent real-time PCR-based genotyping.Clin Chim Acta. 2006 Jan;363(1-2):138-46. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2005.05.044. Epub 2005 Sep 8. Clin Chim Acta. 2006. PMID: 16153621 Review.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using locked nucleic acid (LNA).Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003 Jan;3(1):27-38. doi: 10.1586/14737159.3.1.27. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003. PMID: 12528362 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Construction of a Single-Tube, LATE-PCR, Multiplex Endpoint Assay with Lights-On/Lights-Off Probes for the Detection of Pathogens Associated with Sepsis.J Pathog. 2012;2012:424808. doi: 10.1155/2012/424808. Epub 2012 Dec 26. J Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23326668 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent signatures for variable DNA sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Nov;40(21):e164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks731. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22879378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kainz P. The PCR plateau phase – towards an understanding of its limitations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1494:23–27. - PubMed
-
- Freeman WM, Walker SJ, Vrana KE. Quantitative RT-PCR: pitfalls and potential. Biotechniques. 1999;26:112–125. - PubMed
-
- Morrison C, Gannon F. The impact of the PCR plateau phase on quantitative PCR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1219:493–498. - PubMed
-
- Wong ML, Medrano JF. Real-time PCR for mRNA quantitation. Biotechniques. 2005;39:75–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

