AMPAR removal underlies Abeta-induced synaptic depression and dendritic spine loss
- PMID: 17145504
- PMCID: PMC1850952
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.10.035
AMPAR removal underlies Abeta-induced synaptic depression and dendritic spine loss
Abstract
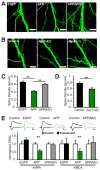
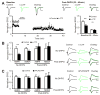
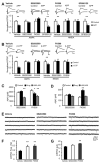
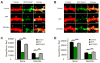
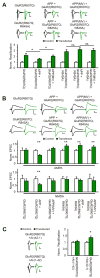
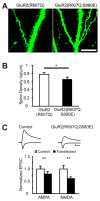
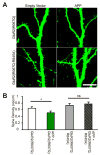
Beta amyloid (Abeta), a peptide generated from the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by neurons, is widely believed to underlie the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease. Recent studies indicate that this peptide can drive loss of surface AMPA and NMDA type glutamate receptors. We now show that Abeta employs signaling pathways of long-term depression (LTD) to drive endocytosis of synaptic AMPA receptors. Synaptic removal of AMPA receptors is necessary and sufficient to produce loss of dendritic spines and synaptic NMDA responses. Our studies indicate the central role played by AMPA receptor trafficking in Abeta-induced modification of synaptic structure and function.
Figures
References
-
- Almeida CG, Tampellini D, Takahashi RH, Greengard P, Lin MT, Snyder EM, Gouras GK. Beta-amyloid accumulation in APP mutant neurons reduces PSD-95 and GluR1 in synapses. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;20:187–198. - PubMed
-
- Baude A, Nusser Z, Roberts JD, Mulvihill E, McIlhinney RA, Somogyi P. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1 alpha) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron. 1993;11:771–787. - PubMed
-
- Beattie EC, Carroll RC, Yu X, Morishita W, Yasuda H, von Zastrow M, Malenka RC. Regulation of AMPA receptor endocytosis by a signaling mechanism shared with LTD. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:1291–1300. - PubMed
-
- Billings LM, Oddo S, Green KN, McGaugh JL, Laferla FM. Intraneuronal Abeta causes the onset of early Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice. Neuron. 2005;45:675–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

