Electrostatic free energy landscapes for nucleic acid helix assembly
- PMID: 17145719
- PMCID: PMC1751542
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl810
Electrostatic free energy landscapes for nucleic acid helix assembly
Abstract
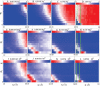
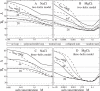
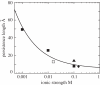
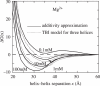
Metal ions are crucial for nucleic acid folding. From the free energy landscapes, we investigate the detailed mechanism for ion-induced collapse for a paradigm system: loop-tethered short DNA helices. We find that Na+ and Mg2+ play distinctive roles in helix-helix assembly. High [Na+] (>0.3 M) causes a reduced helix-helix electrostatic repulsion and a subsequent disordered packing of helices. In contrast, Mg2+ of concentration >1 mM is predicted to induce helix-helix attraction and results in a more compact and ordered helix-helix packing. Mg2+ is much more efficient in causing nucleic acid compaction. In addition, the free energy landscape shows that the tethering loops between the helices also play a significant role. A flexible loop, such as a neutral loop or a polynucleotide loop in high salt concentration, enhances the close approach of the helices in order to gain the loop entropy. On the other hand, a rigid loop, such as a polynucleotide loop in low salt concentration, tends to de-compact the helices. Therefore, a polynucleotide loop significantly enhances the sharpness of the ion-induced compaction transition. Moreover, we find that a larger number of helices in the system or a smaller radius of the divalent ions can cause a more abrupt compaction transition and a more compact state at high ion concentration, and the ion size effect becomes more pronounced as the number of helices is increased.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ion-mediated nucleic acid helix-helix interactions.Biophys J. 2006 Jul 15;91(2):518-36. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.084285. Epub 2006 Apr 28. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16648172 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic free energy landscapes for DNA helix bending.Biophys J. 2008 Apr 15;94(8):3137-49. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.122366. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18192348 Free PMC article.
-
Critical assessment of nucleic acid electrostatics via experimental and computational investigation of an unfolded state ensemble.J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Sep 17;130(37):12334-41. doi: 10.1021/ja800854u. Epub 2008 Aug 23. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18722445 Free PMC article.
-
DNA condensation by multivalent cations.Biopolymers. 1997;44(3):269-82. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1997)44:3<269::AID-BIP6>3.0.CO;2-T. Biopolymers. 1997. PMID: 9591479 Review.
-
Cations as hydrogen bond donors: a view of electrostatic interactions in DNA.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:27-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141726. Epub 2003 Feb 14. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. PMID: 12598364 Review.
Cited by
-
Multivalent ion-mediated nucleic acid helix-helix interactions: RNA versus DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 13;43(12):6156-65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv570. Epub 2015 May 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26019178 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Monovalent Ion Correlation Effects in Nucleic Acids.ACS Omega. 2019 Aug 5;4(8):13435-13446. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b01689. eCollection 2019 Aug 20. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31460472 Free PMC article.
-
Ab initio predictions for 3D structure and stability of single- and double-stranded DNAs in ion solutions.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Oct 19;18(10):e1010501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010501. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36260618 Free PMC article.
-
RNA folding: conformational statistics, folding kinetics, and ion electrostatics.Annu Rev Biophys. 2008;37:197-214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.37.032807.125957. Annu Rev Biophys. 2008. PMID: 18573079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting 3D structures and stabilities for complex RNA pseudoknots in ion solutions.Biophys J. 2023 Apr 18;122(8):1503-1516. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.03.017. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 36924021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bloomfield V.A., Crothers D.M., Tinoco I., Jr . Nucleic Acids: Structure, Properties and Functions. Sausalito, CA: University Science Books; 2000.
-
- Tinoco I., Bustamante C. How RNA folds. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;293:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Anderson C.F., Record M.T., Jr Salt-nucleic acid interactions. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1995;46:657–700. - PubMed
-
- Brion P., Westhof E. Hierarchy and dynamics of RNA folding. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1997;26:113–137. - PubMed
-
- Strobel S.A., Doudna J.A. RNA seeing double: close-packing of helices in RNA tertiary structure. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1997;22:262–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

