RANK overexpression in transgenic mice with mouse mammary tumor virus promoter-controlled RANK increases proliferation and impairs alveolar differentiation in the mammary epithelia and disrupts lumen formation in cultured epithelial acini
- PMID: 17145767
- PMCID: PMC1800710
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01298-06
RANK overexpression in transgenic mice with mouse mammary tumor virus promoter-controlled RANK increases proliferation and impairs alveolar differentiation in the mammary epithelia and disrupts lumen formation in cultured epithelial acini
Abstract
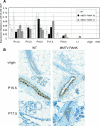
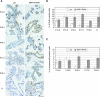
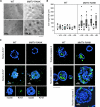
RANK and RANKL, the key regulators of osteoclast differentiation and activation, also play an important role in the control of proliferation and differentiation of mammary epithelial cells during pregnancy. Here, we show that RANK protein expression is strictly regulated in a spatial and temporal manner during mammary gland development. RANK overexpression under the control of the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) promoter in a transgenic mouse model results in increased mammary epithelial cell proliferation during pregnancy, impaired differentiation of lobulo-alveolar structures, decreased expression of the milk proteins beta-casein and whey acidic protein, and deficient lactation. We also show that treatment of three-dimensional in vitro cultures of primary mammary cells from MMTV-RANK mice with RANKL results in increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis in the luminal area, resulting in bigger acini with filled lumens. Taken together, these results suggest that signaling through RANK not only promotes proliferation but also inhibits the terminal differentiation of mammary epithelial cells. Moreover, the increased proliferation and survival observed in a three-dimensional culture system suggests a role for aberrant RANK signaling during breast tumorigenesis.
Figures




References
-
- Anderson, D. M., E. Maraskovsky, W. L. Billingsley, W. C. Dougall, M. E. Tometsko, E. R. Roux, M. C. Teepe, R. F. DuBose, D. Cosman, and L. Galibert. 1997. A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature 390:175-179. - PubMed
-
- Andres, A. C., M. A. van der Valk, C. A. Schonenberger, F. Fluckiger, M. LeMeur, P. Gerlinger, and B. Groner. 1988. Ha-ras and c-myc oncogene expression interferes with morphological and functional differentiation of mammary epithelial cells in single and double transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 2:1486-1495. - PubMed
-
- Arai, F., T. Miyamoto, O. Ohneda, T. Inada, T. Sudo, K. Brasel, T. Miyata, D. M. Anderson, and T. Suda. 1999. Commitment and differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential expression of c-Fms and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB (RANK) receptors. J. Exp. Med. 190:1741-1754. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
