Mechanism of antimalarial action of the synthetic trioxolane RBX11160 (OZ277)
- PMID: 17145800
- PMCID: PMC1797759
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01064-06
Mechanism of antimalarial action of the synthetic trioxolane RBX11160 (OZ277)
Abstract
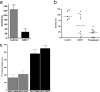
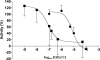
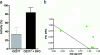
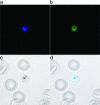
RBX11160 (OZ277) is a fully synthetic peroxidic antimalarial in clinical development. To study the possible mechanisms of action of RBX11160, we have examined its ability to inhibit PfATP6, a sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase and proposed target for semisynthetic peroxidic artemisinin derivatives. RBX11160 inhibits PfATP6 (apparent half-maximal inhibitory constant=7,700 nM) less potently than artemisinin (79 nM). Inhibition of PfATP6 is abrogated by desferrioxamine, an iron-chelating agent. Consistent with this finding, the killing of Plasmodium falciparum organisms by RBX11160 in vitro is antagonized by desferrioxamine. Artesunate and RBX11160 also act antagonistically against P. falciparum in vitro. A fluorescent derivative of RBX11160 localizes to the parasite cytosol in some parasites and to the food vacuole in other parasites. These data demonstrate that there are both similarities and differences between the antimalarial properties of RBX11160 and those of semisynthetic antimalarials such as artesunate and artemisinin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peroxide bond-dependent antiplasmodial specificity of artemisinin and OZ277 (RBx11160).Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Aug;51(8):2991-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00225-07. Epub 2007 Jun 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17562801 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro interaction of artemisinin derivatives or the fully synthetic peroxidic anti-malarial OZ277 with thapsigargin in Plasmodium falciparum strains.Malar J. 2013 Jan 31;12:43. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-43. Malar J. 2013. PMID: 23368889 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the antimalarial mechanism of artemisinin and OZ277 (arterolane) with nonperoxidic isosteres and nitroxyl radicals.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Mar;54(3):1042-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01305-09. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20028825 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations on the mechanism of action of artemisinin antimalarials: part 1--the 'carbon radical' and 'heme' hypotheses.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Aug;13(4):217-77. doi: 10.2174/1871526513666131129155708. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 24304352 Review.
-
Exploration of artemisinin derivatives and synthetic peroxides in antimalarial drug discovery research.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Mar 5;213:113193. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113193. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33508479 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between antimalarial activity and heme alkylation for spiro- and dispiro-1,2,4-trioxolane antimalarials.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Apr;52(4):1291-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01033-07. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18268087 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanism of action of artemisinin--the debate continues.Molecules. 2010 Mar 12;15(3):1705-21. doi: 10.3390/molecules15031705. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20336009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fixed dose combination of arterolane and piperaquine: a newer prospect in antimalarial therapy.Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014 Jul;4(4):466-71. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.139270. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014. PMID: 25221689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal Antibodies That Recognize the Alkylation Signature of Antimalarial Ozonides OZ277 (Arterolane) and OZ439 (Artefenomel).ACS Infect Dis. 2016 Jan 8;2(1):54-61. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5b00090. Epub 2015 Sep 28. ACS Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26819968 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of fixed dose combination of arterolane maleate and piperaquine phosphate dispersible tablets in paediatric patients with acute uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria: a phase II, multicentric, open-label study.Malar J. 2015 Nov 25;14:469. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0982-y. Malar J. 2015. PMID: 26608469 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Eckstein-Ludwig, U., R. J. Webb, I. D. van Goethem, J. M. East, A. G. Lee, M. Kimura, P. M. O'Neill, P. G. Bray, S. A. Ward, and S. Krishna. 2003. Artemisinins target the SERCA of Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 424:957-961. - PubMed
-
- Gu, H. M., D. C. Warhurst, and W. Peters. 1984. Uptake of [3H] dihydroartemisinine by erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 78:265-270. - PubMed
-
- Haynes, R. K. 2006. From artemisinin to new artemisinin antimalarials: biosynthesis, extraction, old and new derivatives, stereochemistry and medicinal chemistry requirements. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 6:509-537. - PubMed
-
- Haynes, R. K., and S. Krishna. 2004. Artemisinins: activities and actions. Microbes Infect. 6:1339-1346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

