Hypervirulence of a rough variant of the Mycobacterium abscessus type strain
- PMID: 17145951
- PMCID: PMC1828507
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00835-06
Hypervirulence of a rough variant of the Mycobacterium abscessus type strain
Abstract
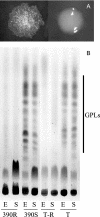
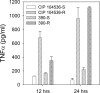
We isolated a rough variant of Mycobacterium abscessus CIP 104536T during experimental infection of mice. We show that this variant has lost the ability to produce glycopeptidolipids, is hyperlethal for C57BL/6 mice infected intravenously, and induces a strong tumor necrosis factor-alpha response by murine monocyte-derived macrophages.
Figures


References
-
- Belisle, J. T., M. R. McNeil, D. Chatterjee, J. M. Inamine, and P. J. Brennan. 1993. Expression of the core lipopeptide of the glycopeptidolipid surface antigens in rough mutants of Mycobacterium avium. J. Biol. Chem. 268:10510-10516. - PubMed
-
- Casanova, J. L., and L. Abel. 2002. Genetic dissection of immunity to mycobacteria: the human model. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20:581-620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

