Dextromethorphan abuse in adolescence: an increasing trend: 1999-2004
- PMID: 17146018
- PMCID: PMC2257867
- DOI: 10.1001/archpedi.160.12.1217
Dextromethorphan abuse in adolescence: an increasing trend: 1999-2004
Abstract
Objectives: To analyze the trend of dextromethorphan abuse in California and to compare these findings with national trends.
Design: A 6-year retrospective review.
Setting: California Poison Control System (CPCS), American Association of Poison Control Centers (AAPCC), and Drug Abuse Warning Network (DAWN) databases from January 1, 1999, to December 31, 2004.
Participants: All dextromethorphan abuse cases reported to the CPCS, AAPCC, and DAWN. The main exposures of dextromethorphan abuse cases included date of exposure, age, acute vs long-term use, coingestants, product formulation, and clinical outcome. Main Outcome Measure The annual proportion of dextromethorphan abuse cases among all exposures reported to the CPCS, AAPCC, and DAWN databases.
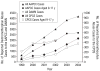
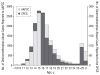
Results: A total of 1382 CPCS cases were included in the study. A 10-fold increase in CPCS dextromethorphan abuse cases from 1999 (0.23 cases per 1000 calls) to 2004 (2.15 cases per 1000 calls) (odds ratio, 1.48; 95% confidence interval, 1.43-1.54) was identified. Of all CPCS dextromethorphan abuse cases, 74.5% were aged 9 to 17 years; the frequency of cases among this age group increased more than 15-fold during the study (from 0.11 to 1.68 cases per 1000 calls). Similar trends were seen in the AAPCC and DAWN databases. The highest frequency of dextromethorphan abuse occurred among adolescents aged 15 and 16 years. The most commonly abused product was Coricidin HBP Cough & Cold Tablets.
Conclusions: Our study revealed an increasing trend of dextromethorphan abuse cases reported to the CPCS that is paralleled nationally as reported to the AAPCC and DAWN. This increase was most evident in the adolescent population.
Figures

References
-
- Ramachander G, Williams FD, Emele JF. Determination of dextrorphan in plasma and evaluation of bioavailability of dextromethorphan hydrobromide in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1977;66:1047–1048. - PubMed
-
- Ginski MJ, Witkin JM. Sensitive and rapid behavioral differentiation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1994;114:573–582. - PubMed
-
- Bobo WV, Fulton RB. Commentary on: severe manifestations of Coricidin intoxication. Am J Emerg Med. 2004;22:624–625. - PubMed
-
- Price LH, Lebel J. Dextromethorphan-induced psychosis [letter] Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:304. - PubMed
-
- Sharma A, Dewan V, Petty F. Acute psychosis with Coricidin cold medicine. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39:1577–1578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

