A chloroplast transgenic approach to hyper-express and purify Human Serum Albumin, a protein highly susceptible to proteolytic degradation
- PMID: 17147744
- PMCID: PMC3481847
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1467-7652.2003.00008.x
A chloroplast transgenic approach to hyper-express and purify Human Serum Albumin, a protein highly susceptible to proteolytic degradation
Abstract
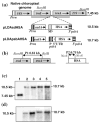
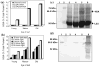
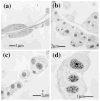
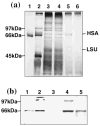
Human Serum Albumin (HSA) accounts for 60% of the total protein in blood serum and it is the most widely used intravenous protein in a number of human therapies. HSA, however, is currently extracted only from blood because of a lack of commercially feasible recombinant expression systems. HSA is highly susceptible to proteolytic degradation in recombinant systems and is expensive to purify. Expression of HSA in transgenic chloroplasts using Shine-Dalgarno sequence (SD), which usually facilitates hyper-expression of transgenes, resulted only in 0.02% HSA in total protein (tp). Modification of HSA regulatory sequences using chloroplast untranslated regions (UTRs) resulted in hyper-expression of HSA (up to 11.1% tp), compensating for excessive proteolytic degradation. This is the highest expression of a pharmaceutical protein in transgenic plants and 500-fold greater than previous reports on HSA expression in transgenic leaves. Electron micrographs of immunogold labelled transgenic chloroplasts revealed HSA inclusion bodies, which provided a simple method for purification from other cellular proteins. HSA inclusion bodies could be readily solubilized to obtain a monomeric form using appropriate reagents. The regulatory elements used in this study should serve as a model system for enhancing expression of foreign proteins that are highly susceptible to proteolytic degradation and provide advantages in purification, when inclusion bodies are formed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tobacco plastidial thioredoxins as modulators of recombinant protein production in transgenic chloroplasts.Plant Biotechnol J. 2011 Aug;9(6):639-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00608.x. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Plant Biotechnol J. 2011. PMID: 21426478
-
Expression and purification of recombinant human serum albumin from selectively terminable transgenic rice.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013 Oct;14(10):867-74. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1300090. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013. PMID: 24101203 Free PMC article.
-
Production of human serum albumin by sugar starvation induced promoter and rice cell culture.Transgenic Res. 2005 Oct;14(5):569-81. doi: 10.1007/s11248-004-6481-5. Transgenic Res. 2005. PMID: 16245148
-
Chloroplast-derived vaccine antigens and other therapeutic proteins.Vaccine. 2005 Mar 7;23(15):1779-83. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.11.004. Vaccine. 2005. PMID: 15734040 Review.
-
Production of biopharmaceuticals and vaccines in plants via the chloroplast genome.Biotechnol J. 2006 Oct;1(10):1071-9. doi: 10.1002/biot.200600145. Biotechnol J. 2006. PMID: 17004305 Review.
Cited by
-
Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) as a novel green-bioreactor for expression of human serum albumin (HSA) gene.Transgenic Res. 2022 Jun;31(3):369-380. doi: 10.1007/s11248-022-00296-9. Epub 2022 May 2. Transgenic Res. 2022. PMID: 35499672
-
Chloroplast transformation of rapeseed (Brassica napus) by particle bombardment of cotyledons.Plant Cell Rep. 2010 Apr;29(4):371-81. doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0828-6. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Plant Cell Rep. 2010. PMID: 20179937
-
Plant plastid engineering.Curr Genomics. 2010 Nov;11(7):500-12. doi: 10.2174/138920210793175912. Curr Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21532834 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Platforms for Efficient Heterologous Protein Production.Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2021;26(4):546-567. doi: 10.1007/s12257-020-0374-1. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2021. PMID: 34393545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of Plastid Expression Vector and Development of Genetic Transformation System for the Seaweed Pyropia yezoensis.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017 Apr;19(2):147-156. doi: 10.1007/s10126-017-9736-x. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017. PMID: 28233074
References
-
- Bogorad L. Engineering chloroplasts: an alternative site for foreign genes, proteins, reactions and products. Trends Biotechnol. 2000;18:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Carrio MM, Corchero JL, Villaverde A. Proteolytic digestion of bacterial inclusion body proteins during dynamic transition between soluble and insoluble forms. Biochim Biophys Act. 1999;1434:170–176. - PubMed
-
- Daniell H. Transformation and foreign gene expression in plants mediated by microprojectile bombardment. Meth Mol Biol. 1997;62:463–489. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

