Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of a new amphotropic murine leukemia virus (MuLV-1313)
- PMID: 17147829
- PMCID: PMC1769482
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-3-101
Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of a new amphotropic murine leukemia virus (MuLV-1313)
Abstract
Background: The amphotropic murine leukemia viruses (MuLV-A's) are naturally occurring, exogenously acquired gammaretroviruses that are indigenous to the Southern California wild mice. These viruses replicate in a wide range of cell types including human cells in vitro and they can cause both hematological and neurological disorders in feral as well as in the inbred laboratory mice. Since MuLV-A's also exhibit discrete interference and neutralization properties, the envelope proteins of these viruses have been extremely useful for studying virus-host cell interactions and as vehicles for transfer of foreign genes into a variety of hosts including human cells. However, the genomic structure of any of the several known MuLV-A's has not been established and the evolutionary relationship of amphotropic retroviruses to the numerous exogenous or endogenous MuLV strains remains elusive. Herein we present a complete genetic structure of a novel amphotropic virus designated MuLV-1313 and demonstrate that this retrovirus together with other MuLV-A's belongs to a distinct molecular, biological and phylogenetic class among the MuLV strains isolated from a large number of the laboratory inbred or feral mice.
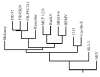
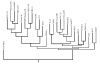
Results: The host range of MuLV-1313 is similar to the previously isolated MuLV-A's except that this virus replicates efficiently in mammalian as well as in chicken cells. Compared to ENV proteins of other MuLV-A's (4070A, 1504A and 10A-1), the gp70 protein of MuLV-1313 exhibits differences in its signal peptides and the proline-rich hinge regions. However, the MuLV-1313 envelope protein is totally unrelated to those present in a broad range of murine retroviruses that have been isolated from various inbred and feral mice globally. Genetic analysis of the entire MuLV-1313 genome by dot plot analyses, which compares each nucleotide of one genome with the corresponding nucleotide of another, revealed that the genome of this virus, with the exception of the env gene, is more closely related to the biologically distinct wild mouse ecotropic retrovirus (Cas-Br-E) isolated from another region of the Southern California, than to any of the 15 MuLV strains whose full-length sequences are present in the GenBank. This finding was corroborated by phylogenetic analyses and hierarchical clustering of the entire genomic sequence of MuLV-1313, which also placed all MULV-A's in a genetically distinct category among the large family of retroviruses isolated from numerous mouse strains globally. Likewise, construction of separate dendrograms for each of the Gag, Pol and Env proteins of MuLV-1313 demonstrated that the amphotropic retroviruses belong to a phylogenetically exclusive group of gammaretroviruses compared to all known MuLV strains.
Conclusion: The molecular, biological and phylogenetic properties of amphotropic retroviruses including MuLV-1313 are distinct compared to a large family of exogenously- or endogenously-transmitted ecotropic, polytropic and xenotropic MuLV strains of the laboratory and feral mice. Further, both the naturally occurring amphotropic and a biologically discrete ecotropic retrovirus of the Southern California wild mice are more closely related to each other on the evolutionary tree than any other mammalian gammaretrovirus indicating a common origin of these viruses. This is the first report of a complete genomic analysis of a unique group of phylogenetically distinct amphotropic virus.
Figures







References
-
- Rasheed S, Toth E, Gardner MB. Characterization of purely ecotropic and amphotropic naturally occurring wild mouse leukemia viruses. Intervirology. 1977;8:323–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

