Prenatal malnutrition alters diazepam-mediated suppression of ultrasonic vocalizations in an age dependent manner
- PMID: 17147960
- PMCID: PMC1975860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.11.018
Prenatal malnutrition alters diazepam-mediated suppression of ultrasonic vocalizations in an age dependent manner
Abstract
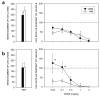
The sensitivity of prenatally malnourished rats to the ultrasonic vocalization (USV) suppressant effect of diazepam (a non-specific benzodiazepine (BZ) receptor agonist) was investigated. Male offspring of dams provided with a protein deficient diet (6% casein) for 5 weeks prior to mating and throughout pregnancy were compared to the offspring of mothers provided with a diet of adequate protein content (25% casein). At postnatal day 7 or 11, pups were injected with vehicle or one of five doses of DZ (0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1 or 3mg/kg) 30 min after removal from their dam. Thirty minutes later they were subjected to 2 min of cooling on a 20 degrees C surface and their USVs were quantified. DZ dose-dependently suppressed USV at both ages. At P7, the USV suppressant effect of DZ was the same for both groups. However, by P11 the prenatally malnourished rats showed significantly greater suppression of USV by 0.03 and 0.1mg/kg DZ than well-nourished controls. These differences were not related to degree of temperature loss or body weight. Thus, differential sensitivity to BZ receptor agonists develops in the second postnatal week in prenatally malnourished rats. This reflects either an altered program of development of the GABAergic system, or adaptive, compensatory changes in the GABAergic system in response to more extensive functional disturbances in the developing brain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultrasonic call characteristics of rat pups are altered following prenatal malnutrition.Dev Psychobiol. 2003 Sep;43(2):90-101. doi: 10.1002/dev.10124. Dev Psychobiol. 2003. PMID: 12918088
-
Zolpidem, triazolam, and diazepam decrease distress vocalizations in mouse pups: differential antagonism by flumazenil and beta-Carboline-3-carboxylate-t-butyl ester (beta-CCt).J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Apr;297(1):247-53. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. PMID: 11259551
-
Diazepam withdrawal: effects of diazepam and gepirone on acoustic startle-induced 22 kHz ultrasonic vocalizations.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1994 Feb;114(1):101-8. doi: 10.1007/BF02245450. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1994. PMID: 7846191
-
Behavioural changes in the offspring of rats exposed to diazepam during gestation.Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 20;177(1-2):67-74. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90550-p. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990. PMID: 2340857
-
Early behavioral effects of lead perinatal exposure in rat pups.Toxicology. 2005 Jul 1;211(1-2):49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.02.007. Epub 2005 Mar 31. Toxicology. 2005. PMID: 15863247
Cited by
-
Prenatal protein level impacts homing behavior in Long-Evans rat pups.Nutr Neurosci. 2016 Jun;19(5):187-95. doi: 10.1179/1476830515Y.0000000001. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Nutr Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 25603489 Free PMC article.
-
Development of translational methods in spectral analysis of human infant crying and rat pup ultrasonic vocalizations for early neurobehavioral assessment.Front Psychiatry. 2011 Oct 24;2:56. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2011.00056. eCollection 2011. Front Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 22028695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida SS, Tonkiss J, Galler JR. Prenatal protein malnutrition affects exploratory behavior of female rats in the elevated plus maze. Physiol Behav. 1996;60:675–680. - PubMed
-
- Almeida SS, Tonkiss J, Galler JR. Prenatal protein malnutrition affects avoidance but not escape behavior in the elevated T-maze test. Physiol Behav. 1996;60:191–195. - PubMed
-
- Atack JR, Wafford KA, Tye SJ, Cook SM, Sohal B, Pike A, Sur C, Melillo D, Bristow L, Bromidge F, Ragan I, Kerby J, Street L, Carling R, Castro JL, Whiting P, Dawson GR, McKernan RM. TPA023 [7-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-(2-ethyl-2H-1,2,4-triazol-3-ylmethoxy)-3-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine], an agonist selective for alpha2- and alpha3-containing GABAA receptors, is a nonsedating anxiolytic in rodents and primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:410–422. - PubMed
-
- Austin KB, Beiswanger C, Bronzino JD, Austin-LaFrance RJ, Galler JR, Morgane PJ. Prenatal protein malnutrition alters behavioral state modulation of inhibition and facilitation in the dentate gyrus. Brain Res Bull. 1992;28:245–255. - PubMed
-
- Austin KB, Bronzino JD, Morgane PJ. Prenatal protein malnutrition affects synaptic potentiation in the dentate gyrus of rats in adulthood. Dev Brain Res. 1986;29:267–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

