Elevated plasma osteopontin associated with gastric cancer development, invasion and survival
- PMID: 17148500
- PMCID: PMC1954839
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2006.109868
Elevated plasma osteopontin associated with gastric cancer development, invasion and survival
Abstract
Objective: Osteopontin (OPN) has been found to be valuable in diagnosis and predicting the prognosis of a variety of malignancies. The aims of the present study are to evaluate the usefulness of plasma OPN level for predicting gastric cancer development, invasion and survival.
Patients and methods: One hundred and thirty two gastric cancer patients and 93 healthy controls were enrolled. Real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical staining were used to detect OPN expression in gastric cancer tissues. Plasma levels of OPN were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Plasma OPN levels were compared with gastric cancer development, clinicopathological features and outcomes.
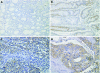
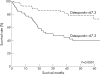
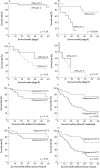
Results: Expression of OPN mRNA was significantly higher in gastric cancer tissues compared with non-tumour tissues. Most OPN immunoactivity was localised to cancer cells. The median plasma OPN level was significantly higher in patients than in controls (p<0.0001), and significantly higher in patients with advanced stages, serosal invasion, lymph node metastasis, lymphatic invasion, venous invasion and liver metastasis. Logistic regression showed that high plasma OPN level (greater than 67.3 ng/ml) is significantly associated with advanced stages, serosal invasion, lymph node metastasis, lymphatic invasion, venous invasion and liver metastasis. Plasma OPN level demonstrated significant association with patient survival (p<0.0001), especially in the subgroups with invasive phenotypes. On Cox multivariate analysis, elevated plasma OPN level was an independent risk factor for poor survival (p<0.0001).
Conclusions: Elevated plasma OPN level is significantly associated with gastric cancer development, invasive phenotypes and survival. Plasma OPN level may have potential usefulness as a diagnostic and prognostic factor for gastric cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest: None.
Similar articles
-
Osteopontin as potential biomarker and therapeutic target in gastric and liver cancers.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 14;18(30):3923-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3923. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22912540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of osteopontin expression in human gastric carcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2007 Dec;14(12):3419-27. doi: 10.1245/s10434-007-9564-8. Epub 2007 Sep 26. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17896150
-
[Expression of osteopontin mRNA and its clinical significance in gastric cancer].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2005 May;27(5):292-5. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15996323 Chinese.
-
Loss of RUNX3 increases osteopontin expression and promotes cell migration in gastric cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2452-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt218. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23774402
-
Osteopontin as a target for cancer therapy.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:4361-72. doi: 10.2741/3009. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508515 Review.
Cited by
-
The prognostic significance of the comprehensive complication index in patients with gastric cancer.Surg Today. 2019 Nov;49(11):913-920. doi: 10.1007/s00595-019-01828-3. Epub 2019 May 30. Surg Today. 2019. PMID: 31147763
-
Serum OPN expression for identification of gastric cancer and atrophic gastritis and its influencing factors.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 5;9(12):e114005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114005. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25479069 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) and Gustave Roussy Immune (GRIm) score with immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy in patients with gastrointestinal and lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 8;24(1):428. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12149-1. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38589844 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin as potential biomarker and therapeutic target in gastric and liver cancers.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 14;18(30):3923-30. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3923. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22912540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers for predicting future metastasis of human gastrointestinal tumors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Oct;70(19):3631-56. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1266-8. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23370778 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gordon D. Luk. Tumors of the stomach. In: Feldman M, ed, Gastrointestinal and liver disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management Philadelphia: WB Saunders 2005733–757.
-
- Roukos D H. Current status and future perspectives in gastric cancer management. Cancer Treat Rev 200026243–255. - PubMed
-
- Kim J P. Surgical results in gastric cancer. Semin Surg Oncol 199917132–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials