Changes in macrophage function after rituximab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17148544
- PMCID: PMC1954671
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.062505
Changes in macrophage function after rituximab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To assess changes in macrophage phenotype and function after rituximab-induced B cell depletion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: 10 patients with RA were treated with rituximab, achieving significant B cell depletion 4 months later. Clinical improvement, rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies, mRNA of B cell activating factor (BAFF), interleukin (IL) 10 and CD86 in human monocyte-derived macrophages (HMDMs) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) secretion from cultured HMDMs were assessed at baseline and after the depletion.
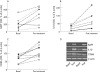
Results: A clinical response of American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 50% improvement was noted in six patients, and another two patients responded with moderate improvement, equivalent to ACR 20-50% improvements. RF and anti-CCP antibodies were positive at baseline in seven of ten patients. RF disappeared or declined in six patients 4 months after treatment, correlating with clinical improvement. By contrast, anti-CCP remained unchanged in six patients. After rituximab treatment, and in association with clinical improvement, BAFF, IL10 and CD86 mRNA expression in HMDM were significantly upregulated compared with values at baseline. A significant decrease in TNFalpha in the supernatant of cultured HMDM was also noted.
Conclusions: In addition to B cell depletion and attenuation in some of the specific autoantibodies, clinical improvement in rituximab-treated patients with RA occurred in association with changes in macrophage function.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
[Rheumatoid factor positivity rather than anti-CCP positivity, a lower disability and a lower number of anti-TNFalpha agents failed are associated with response to rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis].Reumatismo. 2009 Jul-Sep;61(3):182-6. doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2009.182. Reumatismo. 2009. PMID: 19888503 Italian.
-
Synovial tissue response to rituximab: mechanism of action and identification of biomarkers of response.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Jul;67(7):917-25. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.080960. Epub 2007 Oct 26. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 17965121 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inflammation and autoantibody markers identify rheumatoid arthritis patients with enhanced clinical benefit following rituximab treatment.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Dec;63(12):3681-91. doi: 10.1002/art.30596. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 22127691 Clinical Trial.
-
The status of rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody are not associated with the effect of anti-TNFα agent treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 27;9(2):e89442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089442. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rituximab: novel B-cell depletion therapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2006 Dec;7(18):2559-70. doi: 10.1517/14656566.7.18.2559. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 17150009 Review.
Cited by
-
Disease-modifying therapies and SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in multiple sclerosis: an expert consensus.J Neurol. 2021 Nov;268(11):3961-3968. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10545-2. Epub 2021 Apr 12. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33844056 Free PMC article.
-
Increased numbers of CD23(+) CD21(hi) Bin-like B cells in human reactive and rheumatoid arthritis lymph nodes.Eur J Immunol. 2016 Jul;46(7):1752-7. doi: 10.1002/eji.201546266. Epub 2016 May 6. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27105894 Free PMC article.
-
NK and NKT cell dynamics after rituximab therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2009 Feb;29(4):469-75. doi: 10.1007/s00296-008-0719-0. Epub 2008 Sep 28. Rheumatol Int. 2009. PMID: 18821073
-
Restrictive IgG antibody response against mutated citrullinated vimentin predicts response to rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Aug 13;17(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0717-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26268352 Free PMC article.
-
B cells contribute to MS pathogenesis through antibody-dependent and antibody-independent mechanisms.Biologics. 2012;6:117-23. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S24734. Epub 2012 May 7. Biologics. 2012. PMID: 22690126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lipsky P E. Systemic lupus erythematosus: an autoimmune disease of B cell hyperactivity. Nat Immunol 20012764–766. - PubMed
-
- Sfikakis P P, Boletis J N, Tsokos G C. Rituximab anti‐B‐cell therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: pointing to the future. Curr Opin Rheumatol 200517550–557. - PubMed
-
- Crawford A, Macleod M, Schumacher T, Corlett L, Gray D. Primary T cell expansion and differentiation in vivo requires antigen presentation by B cells. J Immunol 20061763498–3506. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical