A system for quantifying dynamic protein interactions defines a role for Herceptin in modulating ErbB2 interactions
- PMID: 17148612
- PMCID: PMC1748177
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0605218103
A system for quantifying dynamic protein interactions defines a role for Herceptin in modulating ErbB2 interactions
Abstract
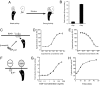
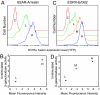
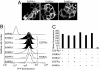
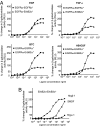
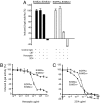
The orphan receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB2 is activated by each of the EGFR family members upon ligand binding. However, difficulties monitoring the dynamic interactions of the membrane receptors have hindered the elucidation of the mechanism of ErbB2 activation. We have engineered a system to monitor protein-protein interactions in intact mammalian cells such that different sets of protein interactions can be quantitatively compared. Application of this system to the interactions of the EGFR family showed that ErbB2 interacts stably with the EGFR and ErbB3, but fails to spontaneously homooligomerize. The widely used anti-cancer antibody Herceptin was found to effectively inhibit the interaction of the EGFR and ErbB2 but not to interfere with the interaction of ErbB2-ErbB3. Treatment of cells expressing EGFR and ErbB2 with Herceptin results in increased EGFR homooligomerization in the presence of EGF and a subsequent rapid internalization and down-regulation of the EGFR. In summary, the protein interaction system described here enabled the characterization of ErbB2 interactions within the biological context of the plasma membrane and provides insight into the mechanism of Herceptin action on cells overexpressing ErbB2.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: H.M.B. is a major stockholder in a company that might have a gain or loss financially through publication of this paper. T.S.W. and H.M.B. are inventors of the technology described in this article; a patent is pending.
Figures
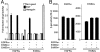
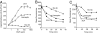
Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor coexpression modulates susceptibility to Herceptin in HER2/neu overexpressing breast cancer cells via specific erbB-receptor interaction and activation.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Apr 1;304(2):604-19. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.12.008. Epub 2005 Jan 21. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15748904
-
Growth stimulation of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by antibody against epidermal growth factor receptor promoting formation of ErbB2/ErbB3 heterodimers.Mol Cancer Res. 2007 Apr;5(4):393-401. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0303. Mol Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17426253
-
Activation of ErbB2 by overexpression or by transmembrane neuregulin results in differential signaling and sensitivity to herceptin.Cancer Res. 2005 Aug 1;65(15):6801-10. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4023. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16061662
-
The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2014 Jan;79:34-74. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Pharmacol Res. 2014. PMID: 24269963 Review.
-
The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling system in development and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2007;190:1-65. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17432114 Review.
Cited by
-
Application guide for omics approaches to cell signaling.Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Jun;11(6):387-97. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1809. Epub 2015 May 15. Nat Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25978996
-
Physiological Considerations for Modeling in vivo Antibody-Target Interactions.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 24;13:856961. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.856961. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35281913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of trastuzumab-resistant human gastric carcinoma cell lines and mechanisms of drug resistance.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 25;5:11634. doi: 10.1038/srep11634. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26108989 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical activities of the epidermal growth factor receptor family inhibitors in breast cancer.Biologics. 2007 Sep;1(3):229-39. Biologics. 2007. PMID: 19707333 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of a novel heterodimeric Fc for bispecific antibody production.Oncotarget. 2017 May 2;8(31):51037-51049. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17558. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Science. 1987;235:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Gschwantler-Kaulich D, Hudelist G, Koestler WJ, Czerwenka K, Mueller R, Helmy S, Ruecklinger E, Kubista E, Singer CF. Oncol Rep. 2005;14:305–311. - PubMed
-
- DiGiovanna MP, Stern DF, Edgerton SM, Whalen SG, Moore D, II, Thor AD. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1152–1160. - PubMed
-
- Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE, Jr, Davidson NE, Tan-Chiu E, Martino S, Paik S, Kaufman PA, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1673–1684. - PubMed
-
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, Gianni L, Baselga J, Bell R, Jackisch C, et al. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1659–1672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 AG009521/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG 020961/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG024987/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HD 018179/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG 0259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AF 051678/AF/ACF HHS/United States
- AG 009521/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008412/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020961/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG009521/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG 024987/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD018179/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000259/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM 08412/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

