Improving influenza vaccination rates of high-risk inner-city children over 2 intervention years
- PMID: 17148632
- PMCID: PMC1687170
- DOI: 10.1370/afm.612
Improving influenza vaccination rates of high-risk inner-city children over 2 intervention years
Abstract
Purpose: Influenza immunization rates among children with high-risk medical conditions are disappointingly low, and relatively few data are available on raising rates, particularly over 2 years. We wanted to determine whether interventions tailored to individual practice sites improve influenza immunization rates among high-risk children in inner-city health centers over 2 years.
Method: A before-after trial to improve influenza immunization of children was conducted at 5 inner-city health centers (residencies and faith-based). Sites selected interventions from a menu (eg, standing orders, patient and clinician reminders, education) proved to increase vaccination rates, which were directed at children aged 2 to 17 years with high-risk medical conditions. Intervention influenza vaccination rates and 1 and 2 years were compared with those of the preintervention year (2001-2002) and of a comparison site.
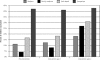
Results: Influenza vaccination rates improved modestly from baseline (10.4%) to 13.1% during intervention year 1 and to 18.7% during intervention year 2 (P <.001), with rates reaching 31% in faith-based practices. Rates increased in all racial and age-groups and in Medicaid-insured children. The increase in rates was significantly greater in intervention health centers (8.3%) than in the comparison health center (0.7%; P <.001). In regression analyses that controlled for demographic factors, vaccination status was associated with intervention year 1 (odds ratio [OR], 1.9; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6-2.2) and with intervention year 2 (OR, 2.8; 95% CI, 2.3-3.4), as well as with practice type. Adolescents had lower vaccination rates than children 2 to 6 years old (OR, 0.6; 95% CI, 0.5-0.7).
Conclusions: Tailored interventions selected from a menu of interventions modestly increased influenza vaccination rates over 2 years at health centers serving children from low-income families. We recommend this strategy for faith-based practices and residencies with 1 practice site, but further research is needed on multisite practices and to achieve higher influenza vaccination rates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tailored interventions to introduce influenza vaccination among 6- to 23-month-old children at inner-city health centers.Am J Manag Care. 2005 Nov;11(11):717-24. Am J Manag Care. 2005. PMID: 16268754
-
Feasibility of influenza immunization for inner-city children aged 6 to 23 months.Am J Prev Med. 2004 Dec;27(5):397-403. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2004.07.016. Am J Prev Med. 2004. PMID: 15556740
-
Effect of a text messaging intervention on influenza vaccination in an urban, low-income pediatric and adolescent population: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2012 Apr 25;307(16):1702-8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.502. JAMA. 2012. PMID: 22535855 Clinical Trial.
-
Update on universal annual influenza immunization recommendations for children.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2009 Feb;21(1):122-6. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e32832185af. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19242248 Review.
-
Distribution of influenza vaccine to high-risk groups.Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28:54-70. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxj004. Epub 2006 May 17. Epidemiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16707648 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Standing Orders for Vaccination Among Pediatricians.Pediatrics. 2020 May;145(5):e20191855. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1855. Pediatrics. 2020. PMID: 32350023 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Impact of Approved but Unfunded Vaccine Status on Parental Acceptance of an Adjuvanted Seasonal Influenza Vaccine for Infants: Results from the Pediatric Influenza Vaccination Optimization Trial (PIVOT)-III.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;10(10):1769. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101769. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298633 Free PMC article.
-
Improving influenza vaccination coverage in the pediatric asthma population: the case for combined methodologies.Yale J Biol Med. 2014 Dec 12;87(4):439-46. eCollection 2014 Dec. Yale J Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 25506278 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Community Health Nurse-Led Intervention on Childhood Routine Immunization Completion in Primary Health Care Centers in Ibadan, Nigeria.J Community Health. 2016 Apr;41(2):265-73. doi: 10.1007/s10900-015-0092-3. J Community Health. 2016. PMID: 26395786
-
Increasing childhood influenza vaccination: a cluster randomized trial.Am J Prev Med. 2014 Oct;47(4):435-43. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Am J Prev Med. 2014. PMID: 25113138 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bridges CB, Fukuda K, Uyeki TM, Cox NJ, Singleton JA. Prevention and control of influenza. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2002;51:1–31. - PubMed
-
- Reduction of the influenza burden in children. Pediatrics. 2002;110:1246–1252. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman RK. Recommended childhood and adolescent immunization schedule, United States, 2003 and update on childhood immunizations. Am Fam Physician. 2003;67:188, 190, 195–186. - PubMed
-
- Harper SA, Fukuda K, Uyeki TM, Cox NJ, Bridges CB. Prevention and control of influenza: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2004;53:1–40. - PubMed
-
- Neuzil KM, Mellen BG, Wright PF, Mitchel EF, Jr., Griffin MR. The effect of influenza on hospitalizations, outpatient visits, and courses of antibiotics in children. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:225–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical