Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application
- PMID: 17148655
- PMCID: PMC1762492
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060681
Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application
Abstract
The intestinal epithelium is faced with the complex task of providing a barrier while also allowing nutrient and water absorption. The frequency with which these processes are disrupted in disease can be taken as evidence of their importance. It is therefore of interest to define the mechanisms of altered intestinal barrier and transport function and develop means to correct disease-associated defects. Over the past 10 years, some of the molecular events underlying physiological epithelial barrier regulation have been described. Remarkably, recent advances have shown that activation of the same mechanisms is central to barrier dysfunction in both in vitro and in vivo models of disease. Although the contribution of barrier dysfunction to pathogenesis of chronic disease remains incompletely understood, it is now clear that cytoskeletal regulation of barrier function is both an important pathogenic process and that targeted inhibition of myosin light chain kinase, which affects this cytoskeleton-dependent tight junction dysfunction, is an attractive candidate for therapeutic intervention.
Figures

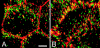
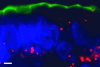
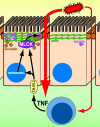
References
-
- Sandler RS, Everhart JE, Donowitz M, Adams E, Cronin K, Goodman C, Gemmen E, Shah S, Avdic A, Rubin R. The burden of selected digestive diseases in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1500–1511. - PubMed
-
- Clayburgh DR, Shen L, Turner JR. A porous defense: the leaky epithelial barrier in intestinal disease. Lab Invest. 2004;84:282–291. - PubMed
-
- Hill GR, Ferrara JL. The primacy of the gastrointestinal tract as a target organ of acute graft-versus-host disease: rationale for the use of cytokine shields in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 2000;95:2754–2759. - PubMed
-
- Baert FJ, D’Haens GR, Peeters M, Hiele MI, Schaible TF, Shealy D, Geboes K, Rutgeerts PJ. Tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody (infliximab) therapy profoundly down-regulates the inflammation in Crohn’s ileocolitis. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:22–28. - PubMed
-
- Suenaert P, Bulteel V, Lemmens L, Noman M, Geypens B, Van Assche G, Geboes K, Ceuppens JL, Rutgeerts P. Anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment restores the gut barrier in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:2000–2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

