Fluorinated conformationally restricted gamma-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase inhibitors
- PMID: 17149870
- PMCID: PMC2577068
- DOI: 10.1021/jm0608715
Fluorinated conformationally restricted gamma-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase inhibitors
Abstract
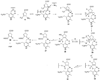
On the basis of the structures of several potent inhibitor molecules for gamma-aminobutryric acid aminotransferase (GABA-AT) that were previously reported, six modified fluorine-containing conformationally restricted analogues were designed, synthesized, and tested as GABA-AT inhibitors. The syntheses of all six molecules followed from a readily synthesized ketone intermediate. Three of the molecules were found to be irreversible inhibitors of GABA-AT with comparable or larger k(inact)/K(I) values than that of vigabatrin, a clinically used antiepilepsy drug, and the other three were reversible inhibitors. A possible mechanism for inactivation by one of the inactivators is proposed.
Figures
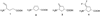
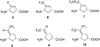
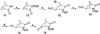
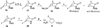


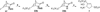
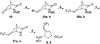
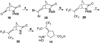


Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and biological activity of a difluoro-substituted, conformationally rigid vigabatrin analogue as a potent gamma-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase inhibitor.J Med Chem. 2003 Dec 4;46(25):5292-3. doi: 10.1021/jm034162s. J Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14640537
-
Inhibition and substrate activity of conformationally rigid vigabatrin analogues with gamma-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase.J Med Chem. 1999 Nov 4;42(22):4725-8. doi: 10.1021/jm990271o. J Med Chem. 1999. PMID: 10579835
-
Syntheses and evaluation of fluorinated conformationally restricted analogues of GABA as potential inhibitors of GABA aminotransferase.Bioorg Med Chem. 2006 Apr 1;14(7):2242-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.11.010. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16314106
-
Design, synthesis, and conformational analysis of azacycloalkane amino acids as conformationally constrained probes for mimicry of peptide secondary structures.Biopolymers. 2000;55(2):101-22. doi: 10.1002/1097-0282(2000)55:2<101::AID-BIP20>3.0.CO;2-O. Biopolymers. 2000. PMID: 11074409 Review.
-
Design of potential anticonvulsant agents: mechanistic classification of GABA aminotransferase inactivators.J Med Chem. 1989 Nov;32(11):2413-21. doi: 10.1021/jm00131a001. J Med Chem. 1989. PMID: 2681782 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inhibition of Overexpressed Ornithine Aminotransferase.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015 May 29;6(8):840-4. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00153. eCollection 2015 Aug 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 26288681 Free PMC article.
-
1,2-(Bis)trifluoromethylation of Alkynes: A One-Step Reaction to Install an Underutilized Functional Group.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Aug 19;58(34):11704-11708. doi: 10.1002/anie.201905247. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31206968 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Syntheses of [11C]Arylvinyltrifluoromethanes through Treatment of (E)-Arylvinyl(phenyl)iodonium Tosylates with [11C]Trifluoromethylcopper(I).Org Lett. 2020 Jun 5;22(11):4574-4578. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01705. Epub 2020 May 27. Org Lett. 2020. PMID: 32459101 Free PMC article.
-
From TgO/GABA-AT, GABA, and T-263 Mutant to Conception of Toxoplasma.iScience. 2023 Nov 16;27(1):108477. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108477. eCollection 2024 Jan 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38205261 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of novel heteroaromatic substrates of GABA aminotransferase.Bioorg Med Chem. 2012 Oct 1;20(19):5763-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.08.009. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22944334 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGeer EG, McGeer PL, Thompson S. GABA and Glutamate Enzymes. In: Hertz L, Kvamme E, McGeer EG, Schousboe A, editors. Glutamine, Glutamate, and GABA in the Central Nervous System. Liss; New York: 1983. pp. 3–17.
-
- Baxter CF, Roberts E. The γ-Aminobutyric Acid-α-Ketoglutaric Acid Transaminase of Beef Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1958;233:1135–1139. - PubMed
-
- Karlsson A, Fonnum F, Malthe-Sorrensen D, Storm-Mathisen J. Effect of the convulsive agent 3-mercaptopropionic acid on the levels of GABA, other amino acids and glutamate decarboxylase in different regions of the rat brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1974;23:3053–3061. - PubMed
-
- Gale K. GABA in epilepsy: the pharmacologic basis. Epilepsia. 1989;30(Suppl 3):S1–S11. - PubMed
-
- Bakay RAE, Harris AB. Neurotransmitter, receptor and biochemical changes in mondey cortical epileptic foci. Brain Res. 1981;206:387–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

