Cholesterol is critical for Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A trafficking and protein stability
- PMID: 17150237
- PMCID: PMC1868700
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.10.046
Cholesterol is critical for Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A trafficking and protein stability
Abstract
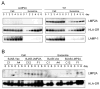
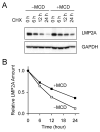
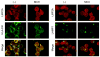
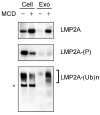
Latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) plays a key role in regulating viral latency and EBV pathogenesis by functionally mimicking signals induced by the B cell receptor (BCR) altering normal B cell development. LMP2A specifically associates with Nedd4 family ubiquitin-protein ligases which downmodulate LMP2A activity by ubiquitinating LMP2A and LMP2A-associated protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). Since specific ubiquitin tags provide an endocytic sorting signal for plasma membrane proteins which traffic to membrane vesicles, we examined LMP2A localization and trafficking. We found that LMP2A is secreted through exosomes, small endocytic membrane vesicles, as previously demonstrated for LMP1. Interestingly, the treatment of cells with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MCD), which depletes cholesterol from plasma membrane, dramatically increased LMP2A abundance and LMP2A exosome secretion. Cholesterol depletion also blocked LMP2A endocytosis resulting in the accumulation of LMP2A on plasma membrane. LMP2A phosphorylation and ubiquitination were blocked by cholesterol depletion. LMP2A in the exosomal fraction was ubiquitinated but not phosphorylated. These results indicate that cholesterol-dependent LMP2A trafficking determines the fate of LMP2A degradation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A PY motif recruits WW domain-containing ubiquitin-protein ligases.Virology. 2000 Mar 1;268(1):178-91. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.0166. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10683340
-
PY motifs of Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A regulate protein stability and phosphorylation of LMP2A-associated proteins.J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(12):5711-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.12.5711-5718.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11356981 Free PMC article.
-
Global Proteomic Changes Induced by the Epstein-Barr Virus Oncoproteins Latent Membrane Protein 1 and 2A.mBio. 2018 Jun 19;9(3):e00959-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00959-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29921667 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus protein LMP2A regulates reactivation from latency by negatively regulating tyrosine kinases involved in sIg-mediated signal transduction.Infect Agents Dis. 1994 Apr-Jun;3(2-3):128-36. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. PMID: 7812651 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A: regulating cellular ubiquitination processes for maintenance of viral latency?Trends Immunol. 2004 Aug;25(8):422-6. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2004.05.009. Trends Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15275641 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A increases IL-10 production in mitogen-stimulated primary B-cells and B-cell lymphomas.J Gen Virol. 2013 May;94(Pt 5):1127-1133. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.049221-0. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Gen Virol. 2013. PMID: 23303827 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles in host-pathogen interactions.EMBO Rep. 2015 Jan;16(1):24-43. doi: 10.15252/embr.201439363. Epub 2014 Dec 8. EMBO Rep. 2015. PMID: 25488940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane elasticity modulated by cholesterol in model of porcine eye lens-lipid membrane.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Jul;220:109131. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109131. Epub 2022 May 27. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 35636489 Free PMC article.
-
The EBV-encoded latent membrane proteins, LMP2A and LMP2B, limit the actions of interferon by targeting interferon receptors for degradation.Oncogene. 2009 Nov 5;28(44):3903-14. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.249. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19718044 Free PMC article.
-
The B subunit of Escherichia coli enterotoxin helps control the in vivo growth of solid tumors expressing the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A.Cancer Med. 2015 Mar;4(3):457-71. doi: 10.1002/cam4.380. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Cancer Med. 2015. PMID: 25641882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aviel S, Winberg G, Massucci M, Ciechanover A. Degradation of the epstein-barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Targeting via ubiquitination of the N-terminal residue. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(31):23491–9. - PubMed
-
- Bloom J, Amador V, Bartolini F, DeMartino G, Pagano M. Proteasome-mediated degradation of p21 via N-terminal ubiquitinylation. Cell. 2003;115(1):71–82. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell RG, Wilson JB, Anderson SJ, Longnecker R. Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A drives B cell development and survival in the absence of normal B cell receptor signals. Immunity. 1998;9(3):405–11. - PubMed
-
- Casola S, Otipoby KL, Alimzhanov M, Humme S, Uyttersprot N, Kutok JL, Carroll MC, Rajewsky K. B cell receptor signal strength determines B cell fate. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(3):317–27. Epub 2004 Feb 1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

