Antibiotic administration early in life impairs specific humoral responses to an oral antigen and increases intestinal mast cell numbers and mediator concentrations
- PMID: 17151185
- PMCID: PMC1797787
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00055-06
Antibiotic administration early in life impairs specific humoral responses to an oral antigen and increases intestinal mast cell numbers and mediator concentrations
Abstract
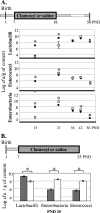
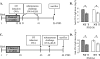
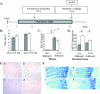
In this study, we assessed the effect of administering the antibiotic amoxicillin to rat pups on the immune response to orally fed ovalbumin (OVA). We first established that amoxicillin administration durably altered the gut microbiota of these animals. In parallel, we observed that the induction of the specific humoral response to ovalbumin was impaired when it occurred during antibiotic administration to the rat pups. We also examined the consequences of those observations on further allergic reactions. Amoxicillin administration had no significant impact on subsequent sensitization to OVA, as nonexacerbated systemic allergic responses were induced in antibiotic-treated animals. However, increased rat mast cell protease II levels and higher mast cell numbers were detected in their small intestines, independently of the antigen administration. Globally, our data suggest that antibiotic administration early in life negatively affects the specific immune response to a luminal antigen when it is first introduced during antibiotic administration. The increased mast cell numbers and mediator concentrations in the intestinal mucosae of the antibiotic-treated animals may testify to the early stages of an altered immune system homeostasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mucosal mast cells mediate motor response induced by chronic oral exposure to ovalbumin in the rat gastrointestinal tract.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010 Jan;22(1):e34-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01377.x. Epub 2009 Aug 13. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010. PMID: 19682267
-
Neonatal antibiotic treatment alters gastrointestinal tract developmental gene expression and intestinal barrier transcriptome.Physiol Genomics. 2005 Oct 17;23(2):235-45. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00057.2005. Epub 2005 Aug 30. Physiol Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16131529
-
Hypersensitivity to ovalbumin induces chronic intestinal dysmotility and increases the number of intestinal mast cells.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2005 Feb;17(1):112-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2004.00597.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2005. PMID: 15670271
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
-
Cannabinomimetic control of mast cell mediator release: new perspective in chronic inflammation.J Neuroendocrinol. 2008 May;20 Suppl 1:20-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01674.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18426495 Review.
Cited by
-
Early changes in microbial colonization selectively modulate intestinal enzymes, but not inducible heat shock proteins in young adult Swine.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 4;9(2):e87967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087967. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24505340 Free PMC article.
-
The intestinal flora is required to support antibody responses to systemic immunization in infant and germ free mice.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027662. Epub 2011 Nov 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22114681 Free PMC article.
-
Partially Hydrolysed Whey Has Superior Allergy Preventive Capacity Compared to Intact Whey Regardless of Amoxicillin Administration in Brown Norway Rats.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 31;12:705543. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.705543. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34531857 Free PMC article.
-
Role of postnatal acquisition of the intestinal microbiome in the early development of immune function.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010 Sep;51(3):262-73. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181e1a114. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20639773 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of neonatal antibiotic treatment on the biodiversity of the murine intestinal Lactobacillus community.Curr Microbiol. 2010 Jan;60(1):6-11. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9492-x. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Curr Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19768504
References
-
- Albu, R. E. 1998. Amoxicillin: a pharmacologic description. Clin. Excell. Nurse Pract. 2:260-262. - PubMed
-
- Bashir, M. E., S. Louie, H. N. Shi, and C. Nagler-Anderson. 2004. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling by intestinal microbes influences susceptibility to food allergy. J. Immunol. 172:6978-6987. - PubMed
-
- Bennet, R., M. Eriksson, and C. E. Nord. 2002. The fecal microflora of 1-3-month-old infants during treatment with eight oral antibiotics. Infection 30:158-160. - PubMed
-
- Bjorksten, B., P. Naaber, E. Sepp, and M. Mikelsaar. 1999. The intestinal microflora in allergic Estonian and Swedish 2-year-old children. Clin. Exp. Allergy 29:342-346. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

