Vaccinia virus inhibits T cell receptor-dependent responses by human gammadelta T cells
- PMID: 17152007
- PMCID: PMC2600876
- DOI: 10.1086/509823
Vaccinia virus inhibits T cell receptor-dependent responses by human gammadelta T cells
Abstract
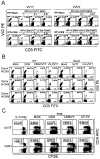
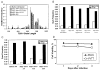
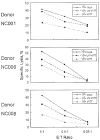
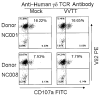
Vaccinia virus (VV) is an effective vaccine and vector but has evolved multiple mechanisms for evading host immunity. We characterized the interactions of VV (TianTan and New York City Board of Health strains) with human gammadelta T cells because of the role they play in immune control of this virus. Exposure to VV failed to trigger proliferative responses in gammadelta T cells from unprimed individuals, but it was an unexpected finding that VV blocked responses to model antigens by the Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cell subset. Infectious or ultraviolet light-inactivated VV inhibited proliferative Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cell responses to phosphoantigens and tumor cells, prevented cytolysis of Daudi B cells, and reduced cytokine production. Inhibiting Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells may be a mechanism for evading host immunity and increasing VV virulence. Increased VV replication or expression in the absence of gammadelta T cell responses might contribute to its potency as a vaccine against poxvirus and recombinant antigens.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: none reported.
Figures

References
-
- Fenner F. History of international public health. 6. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1988. World Health Organization. Smallpox and its eradication.
-
- Haga IR, Bowie AG. Evasion of innate immunity by vaccinia virus. Parasitology. 2005;130(Suppl):S11–25. - PubMed
-
- Seet BT, Johnston JB, Brunetti CR, et al. Poxviruses and immune evasion. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:377–423. - PubMed
-
- Kirwan S, Merriam D, Barsby N, McKinnon A, Burshtyn DN. Vaccinia virus modulation of natural killer cell function by direct infection. Virology. 2006;347:75–87. - PubMed

