Morphine stimulates CCL2 production by human neurons
- PMID: 17156455
- PMCID: PMC1712222
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-3-32
Morphine stimulates CCL2 production by human neurons
Abstract
Background: Substances of abuse, such as opiates, have a variety of immunomodulatory properties that may influence both neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disease processes. The chemokine CCL2, which plays a pivotal role in the recruitment of inflammatory cells in the nervous system, is one of only a few chemokines produced by neurons. We hypothesized that morphine may alter expression of CCL2 by human neurons.
Methods: Primary neuronal cell cultures and highly purified astrocyte and microglial cell cultures were prepared from human fetal brain tissue. Cell cultures were treated with morphine, and cells were examined by RNase protection assay for mRNA. Culture supernatants were assayed by ELISA for CCL2 protein. beta-funaltrexamine (beta-FNA) was used to block mu-opioid receptor (MOR)s.
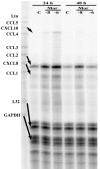
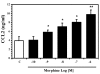
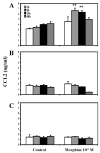
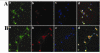
Results: Morphine upregulated CCL2 mRNA and protein in neuronal cultures in a concentration- and time-dependent fashion, but had no effect on CCL2 production in astrocyte or microglial cell cultures. Immunocytochemical analysis also demonstrated CCL2 production in morphine-stimulated neuronal cultures. The stimulatory effect of morphine was abrogated by beta-FNA, indicating an MOR-mediated mechanism.
Conclusion: Morphine stimulates CCL2 production by human neurons via a MOR-related mechanism. This finding suggests another mechanism whereby opiates could affect neuroinflammatory responses.
Figures

References
-
- Nath A, Hauser KF, Wojna V, Booze RM, Maragos W, Prendergast M, Cass W, Turchan JT. Molecular basis for interactions of HIV and drugs of abuse. Journal of acquired immune deficiency syndromes (1999) 2002;31 Suppl 2:S62–9. - PubMed
-
- Wetzel MA, Steele AD, Eisenstein TK, Adler MW, Henderson EE, Rogers TJ. Mu-opioid induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, RANTES, and IFN-gamma-inducible protein-10 expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 2000;165:6519–6524. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

