Antibody induction of lupus-like neuropsychiatric manifestations
- PMID: 17156859
- PMCID: PMC1847384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.10.017
Antibody induction of lupus-like neuropsychiatric manifestations
Erratum in
- J Neuroimmunol. 2007 Dec;192(1-2):235
Abstract
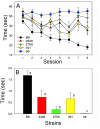
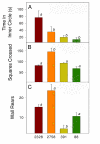
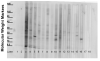
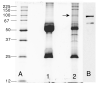
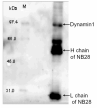
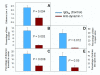
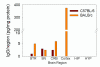
Although systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is usually evaluated with regard to autoimmune reactivity toward the kidney, there are multiple psychiatric abnormalities associated with this autoimmune disease. Lupus-prone male NZM88 mice, derived from NZB/NZW F1 mice, develop early neuropsychiatric manifestations without any signs of nephritis. In addition to the usual repertoire of antibody specificities, including autoantibodies to dsDNA and renal antigens, mice of this inbred strain express autoantibodies to numerous brain antigens. Here, we show that autoantibodies to brain antigens, assessed by Western analysis, are as individually varied as are the diverse neuropsychiatric manifestations observed in SLE patients. Additionally, a monoclonal antibody derived from the spleen of an untreated NZM88 male when injected into healthy BALB/cByJ, but not C57BL/6J, mice induced behaviors similar to those of lupus-prone NZM88 mice. This monoclonal antibody, which is specific to dynamin-1, binds preferentially in BALB/cByJ cortex and induces substantial expression of cytokines mainly in the hypothalamus. Thus, an antibody to just one brain antigen can induce multiple behavioral changes, and multiple autoantibodies to different brain antigens exist in lupus-prone mice; however, susceptibility to the induction of neurobehavioral deficits is dependent on host genetics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Autoantibody-mediated neuroinflammation: pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus in the NZM88 murine model.Brain Behav Immun. 2008 Aug;22(6):949-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2008.01.013. Epub 2008 Apr 14. Brain Behav Immun. 2008. PMID: 18411022
-
Susceptibility of lupus-prone NZM mouse strains to lead exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus symptoms.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2003 May 23;66(10):895-918. doi: 10.1080/15287390306456. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2003. PMID: 12825236
-
Characterization of reactivity of monoclonal autoantibodies with renal antigens in experimental lupus nephritis.J Clin Lab Immunol. 1996;48(5):201-18. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1996. PMID: 9394243
-
Autoantibodies to nervous system tissue in human and murine systemic lupus erythematosus.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997 Aug 14;823:289-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb48402.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997. PMID: 9292056 Review. No abstract available.
-
Neuropsychiatric SLE: from animal model to human.Lupus. 2017 Apr;26(5):470-477. doi: 10.1177/0961203317694261. Lupus. 2017. PMID: 28394237 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-alpha-internexin autoantibody from neuropsychiatric lupus induce cognitive damage via inhibiting axonal elongation and promote neuron apoptosis.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 15;5(6):e11124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011124. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20559547 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: deciphering the complexity and guiding therapeutic development.Autoimmunity. 2024 Dec;57(1):2330387. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2024.2330387. Epub 2024 Mar 31. Autoimmunity. 2024. PMID: 38555866 Review.
-
Diagnosis and early detection of CNS-SLE in MRL/lpr mice using peptide microarrays.BMC Immunol. 2014 Jun 7;15:23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-15-23. BMC Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24908187 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating brain-reactive autoantibodies and behavioral deficits in the MRL model of CNS lupus.J Neuroimmunol. 2010 Jan 25;218(1-2):73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2009.10.008. Epub 2009 Nov 17. J Neuroimmunol. 2010. PMID: 19919882 Free PMC article.
-
Depression is an early disease manifestation in lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice.J Neuroimmunol. 2009 Feb 15;207(1-2):45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.11.009. Epub 2009 Jan 3. J Neuroimmunol. 2009. PMID: 19121871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ainiala H, Loukkola J, Peltola J, Korpela M, Hietaharju A. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurology. 2001;57:496–500. - PubMed
-
- American College of Rheumatology The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Bankhurst AD, Brooks WM. The incidence and prevalence of neuropsychiatric syndromes in pediatric onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2002;29:1536–1542. - PubMed
-
- Bleiberg J, Bunning R. Cognitive and physical measures in rehabilitation of patients with lupus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1998;10:442–445. - PubMed
-
- Bluestein HG, Williams GW, Steinberg AD. Cerebrospinal fluid antibodies to neuronal cells: association with neuropsychiatric manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Med. 1981;70:240–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

