Molecular evidence and functional expression of a novel drug efflux pump (ABCC2) in human corneal epithelium and rabbit cornea and its role in ocular drug efflux
- PMID: 17156953
- PMCID: PMC1995119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.11.031
Molecular evidence and functional expression of a novel drug efflux pump (ABCC2) in human corneal epithelium and rabbit cornea and its role in ocular drug efflux
Abstract
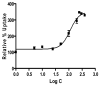
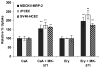
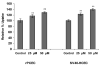
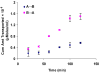
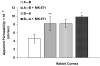
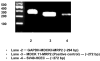
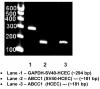
Cornea is considered as a major barrier for ocular drug delivery. Low ocular bioavailability of drugs has been attributed primarily to low permeability across corneal epithelium, thus leading to sub-therapeutic concentrations of drug in the eye and treatment failure. The role of drug efflux proteins, particularly the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in ocular drug bioavailability has been reported. The objective of this research was to determine whether human corneal epithelium expresses multidrug resistance associated proteins (MRPs) contributing to drug efflux by employing both cultured corneal cells and freshly excised rabbit cornea. SV40-HCEC and rPCEC were selected for in vitro testing. SV40-HCEC and freshly excised rabbit corneas were utilized for transport studies. [(3)H]-cyclosporine-A and [(14)C]-erythromycin, which are known substrates for ABCC2 and MK-571, a specific inhibitor for MRP were applied in this study. RT-PCR indicated a unique and distinct band at approximately 272 bp corresponding to ABCC2 in HCEC, SV40-HCEC, rabbit cornea, rPCEC, and MDCKII-MRP2 cells. Also RT-PCR indicated a unique band approximately 181 bp for HCEC and SV40-HCEC. Immunoprecipitation followed by Western Blot analysis revealed a specific band at approximately 190 kDa in membrane fraction of SV40-HCEC, MDCKII-MRP2 and no band with isotype control. Uptake of [(3)H]-cyclosporine-A and [(14)C]-erythromycin in the presence of MK-571 was significantly enhanced than control in both SV40-HCEC and rPCEC. Similarly a significant elevation in (A-->B) permeability of [(3)H]-cyclosporine-A and [(14)C]-erythromycin was observed in the presence of MK-571 in SV40-HCEC. A-->B transport of [(3)H]-cyclosporine-A was elevated in the presence of MK-571 in freshly excised rabbit cornea indicating potential role of this efflux transporter and high clinical significance of this finding.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Molecular expression and functional evidence of a drug efflux pump (BCRP) in human corneal epithelial cells.Curr Eye Res. 2009 Jan;34(1):1-9. doi: 10.1080/02713680802518251. Curr Eye Res. 2009. PMID: 19172464 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of multidrug resistance associated protein 5 (MRP5) on cornea and its role in drug efflux.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Apr;25(2):121-32. doi: 10.1089/jop.2008.0084. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19323627 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular evidence and functional expression of multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP) in rabbit corneal epithelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2007 Jan;84(1):53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2006.08.015. Epub 2006 Nov 2. Exp Eye Res. 2007. PMID: 17083930
-
MDR- and CYP3A4-mediated drug-drug interactions.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;1(3):323-39. doi: 10.1007/s11481-006-9034-2. Epub 2006 Aug 2. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 18040809 Review.
-
[Cultured human corneal endothelial cell transplantation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2006 Nov;110(11):879-97. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 17134036 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Effect of emergence of fluoroquinolone resistance on intrinsic expression of P-glycoprotein phenotype in corneal epithelial cells.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Dec;27(6):553-9. doi: 10.1089/jop.2011.0076. Epub 2011 Aug 10. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21830912 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced corneal absorption of erythromycin by modulating P-glycoprotein and MRP mediated efflux with corticosteroids.Pharm Res. 2009 May;26(5):1270-82. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9741-x. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Pharm Res. 2009. PMID: 18958406 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular expression and functional evidence of a drug efflux pump (BCRP) in human corneal epithelial cells.Curr Eye Res. 2009 Jan;34(1):1-9. doi: 10.1080/02713680802518251. Curr Eye Res. 2009. PMID: 19172464 Free PMC article.
-
Prodrug approach to improve absorption of prednisolone.Int J Pharm. 2015 Jun 20;487(1-2):242-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.04.029. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25888804 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular cytochrome P450s and transporters: roles in disease and endobiotic and xenobiotic disposition.Drug Metab Rev. 2014 Aug;46(3):247-60. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2014.921190. Epub 2014 May 26. Drug Metab Rev. 2014. PMID: 24856391 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Araki-Sasaki K, Ohashi Y, Sasabe T, Hayashi K, Watanabe H, Tano Y, Handa H. An SV40-immortalized human corneal epithelial cell line and its characterization. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1995;36:614–21. - PubMed
-
- Barza M, Kane A, Baum J. Comparison of the effects of continuous and intermittent systemic administration on the penetration of gentamicin into infected rabbit eyes. J. Infect. Dis. 1983;147:144–148. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Bredel M, Bredel C, Sikic BI. Genomics-based hypothesis generation: a novel approach to unraveling drug resistance in brain tumors. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:89–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

