Yng1 PHD finger binding to H3 trimethylated at K4 promotes NuA3 HAT activity at K14 of H3 and transcription at a subset of targeted ORFs
- PMID: 17157260
- PMCID: PMC4690528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.10.026
Yng1 PHD finger binding to H3 trimethylated at K4 promotes NuA3 HAT activity at K14 of H3 and transcription at a subset of targeted ORFs
Abstract
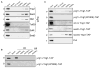
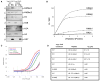
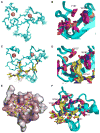
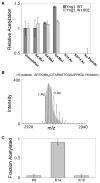
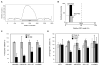
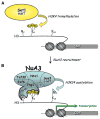
Posttranslational histone modifications participate in modulating the structure and function of chromatin. Promoters of transcribed genes are enriched with K4 trimethylation and hyperacetylation on the N-terminal tail of histone H3. Recently, PHD finger proteins, like Yng1 in the NuA3 HAT complex, were shown to interact with H3K4me3, indicating a biochemical link between K4 methylation and hyperacetylation. By using a combination of mass spectrometry, biochemistry, and NMR, we detail the Yng1 PHD-H3K4me3 interaction and the importance of NuA3-dependent acetylation at K14. Furthermore, genome-wide ChIP-Chip analysis demonstrates colocalization of Yng1 and H3K4me3 in vivo. Disrupting the K4me3 binding of Yng1 altered K14ac and transcription at certain genes, thereby demonstrating direct in vivo evidence of sequential trimethyl binding, acetyltransferase activity, and gene regulation by NuA3. Our data support a general mechanism of transcriptional control through which histone acetylation upstream of gene activation is promoted partially through availability of H3K4me3, "read" by binding modules in select subunits.
Figures

References
-
- Agalioti T, Chen G, Thanos D. Deciphering the transcriptional histone acetylation code for a human gene. Cell. 2002;111:381–392. - PubMed
-
- Bienz M. The PHD finger, a nuclear protein-interaction domain. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM076547/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015569/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR022220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR022220/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM063959/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR016460/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM076547/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM63959/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA09673/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM053512/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM53512/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009673/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RR00862/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR016460/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR015569/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

